
Sustainability is at the heart of Ambuja Cements' strategy, risk management and innovation. To decarbonise the value chain, the Company invests in green power, reduces reliance on fossil fuels with alternative fuels and champions circularity through waste-derived resources amongst other initiatives. The Company’s strong Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework transforms climate risks into opportunities for innovation and gaining a competitive edge. It is committed to Net Zero by 2050 in alignment with the Paris Agreement. The Company advances multiple UNSDGs across the pillars of sustainability. This commitment not only supports environmental goals but also cements the Company's leadership in industry transformation and innovation.
Focus Areas
| Net Zero | Energy Efficiency | Water Positivity | Waste Management and Circular Economy |
Biodiversity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Development and Key Initiatives
|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Performance Indicators FY 2024-25
537 kg/tonne
of Cementitious Material Scope 1 emissions
17 kg/tonne
of Cementitious Material Scope 2 Emissions
28%
Renewable and Green Power |
757 kCal/kg
of Clinker-specific Thermal Energy Consumption
76 kwh/tonne
of Specific Electrical Energy Consumption |
12x
Water Positive
>50%
Operational Water Requirement Met through Harvested Rainwater
172 litres
Per Tonne of Cementitious Material used in |
8.1 million tonnes
of Waste-derived Resources
11x
Plastic Negative |
1.08 lakhs
(1.5 million till FY 2024-25) Trees planted No Net Deforestation |
Material Topics
- 1 Climate and Energy
- 2 Air Quality
- 3 Water Management
- 4 Circular Economy
- 5 Biodiversity Management
- 6 Sustainable Construction
Stakeholders Impacted
-
 Communities and NGOs
Communities and NGOs
-
 Government and
Regulatory Authorities
Government and
Regulatory Authorities
-
 Suppliers
Suppliers
-
 Channel Partners
Channel Partners
-
 Employees
Employees
SDGs Impacted
Sustainability Strategy
At Ambuja Cements, sustainability is deeply embedded in its corporate strategy, guided by well-defined policies and a commitment to setting industry benchmarks.
Ambuja Cements prioritises responsible growth, resilience and a strong commitment to sustainability. In the hard-to-abate cement sector, Ambuja and its subsidiary ACC Limited are the only two companies in India that have committed to SBTi for Net Zero GHG carbon emissions by 2050, ahead of the country’s commitment to be Net Zero by 2070.
Strong Governance for Sustainability Oversight
- Corporate Responsibility Committee: Oversees sustainability agenda and climate change mitigation.
- Independent Directors: Provide guidance on long-term targets.
- Senior Management: Leads execution of sustainability initiatives, aligning with business goals.
- Regular Monitoring: Ensures continuous improvement and accountability by management and the Board.
Environmental Policy and Management System
Ambuja Cements' robust Environmental Management System strengthens sustainability through key enablers:
- Policy Alignment: Aligns policies and procedures with industry-leading standards.
- Climate Risk Management: Proactively identifies and manages climate risks.
- Waste Reduction: Implements measures to minimise waste generation.
- Recycling Promotion: Encourages recycling and resource efficiency.
The Company actively promotes the integration of climate change measures with national and global policies, demonstrating its commitment to broader environmental initiatives and sustainable practices. These policies apply to all of the Company’s operations, with implementation overseen by the Corporate Responsibility Committee (CRC), which consists of Independent Directors and is accountable to the Board.


| Performance Highlights for FY 2024-25 | ||
|---|---|---|

Net Zero
Commitment By 2050 with nearterm |

537 kg/tonne
of Cementitious
materials |

17 kg/tonne
of Cementitious
materials |
28%
Renewable and |
8.1 MMT
Of Waste-derived Resources |
12x
Water-positive |

11x
Plastic-negative |

1.5 million
Trees planted till FY '25 |

67%
Clinker Factor |
Climate and Energy
Climate Strategy
Ambuja Cements' climate initiatives are aligned with both national and international frameworks, including the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs).With a focus on reducing its carbon footprint, building resilience, and achieving Net Zero emissions, Ambuja Cements has conducted a comprehensive climate risk assessment for all its plants, following TCFD and IFRS S2 guidelines. This assessment has identified physical and transitional risks, enabling the development of targeted mitigation strategies to address climate change impacts and enhance business resilience.
The assessment has also helped us in identifying opportunities and taking initiatives to mainstream the opportunities into business e.g. use of renewable energy, setting up of Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS).
Climate Governance
The Board and senior leadership team conduct quarterly reviews to assess progress against the Company’s goals and targets. This ongoing monitoring allows for timely adjustments to ensure Ambuja Cements meets its objectives. The Corporate Responsibility Committee (CRC), which includes Independent Directors, oversees sustainability initiatives and tracks climate-related key performance indicators (KPIs).
Senior management ensures the integration of the Company’s broader sustainability strategy, with support from the ESG team, which drives and implements the ESG agenda. The Risk Management Committee (RMC) oversees sustainability and ESG-related risks. Climate-related risks have become a core component of the Company’s enterprise risk management process, with performance improvements discussed during CEO and COO plant visits.
Climate Risks and Mitigation
The Company recognises the climate-related risks it faces, including escalating regulatory pressures, rising energy costs, and physical risks such as extreme weather events that disrupt production and supply chains. Additionally, there is increasing demand for reduced carbon emissions in cement manufacturing. To address these risks and ensure business continuity, Ambuja Cements has integrated climate change risks into its comprehensive Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) strategy. A detailed Climate Change Risk Assessment has been conducted, covering short-, medium-, and long-term timeframes. Ambuja Cements Limited considers both, physical risks caused by the increased frequency and severity of climate and weather events, and transitional risks associated with economic, technology or regulatory changes. While these challenges pose significant risks, they also present opportunities for innovation, sustainability leadership, and gaining a competitive edge.
Physical Risks
Ambuja Cements conducted a comprehensive climate risk assessment across all its sites, evaluating physical risks such as flooding, droughts, cyclones and wildfires under IPCC scenarios SSP1-2.6, SSP2-4.5 and SSP5-8.5. Shared Socio-economic Pathways (SSPs) is the latest set of emission scenarios used in climate modelling. This analysis provided the Company with valuable insights into potential impacts, enabling the development of effective strategies to mitigate risks associated with different greenhouse gas emission pathways.

List of Physical Risks
| Risk Category | Risk Subcategory | Risk Description |
| Acute Physical Risks | Flood Pluvial | Excessive rainfall can result in pluvial flooding, causing substantial damage and operational disruptions. |
| Cyclone | Over the past four decades, the frequency of intense cyclones (Category 3 and above) has steadily increased. If this trend persists with climate change, the heightened wind speeds of these storms could pose severe threats to infrastructure and assets, potentially causing catastrophic damage. | |
| Wildfire | Temperature and precipitation patterns significantly influence conditions that promote wildfires. Rising temperatures make wildfire-prone regions warmer and drier, increasing the likelihood of intense wildfires, which pose serious risks to assets and may result in potential shutdowns. | |
| Chronic Physical Risks | Extreme Temperature | Global warming, driven by climate change, has caused a wide array of consequences. Rising temperatures worldwide have triggered numerous far-reaching impacts. |
| Water Stress | Ongoing water scarcity can exacerbate climate change impacts, leading to more frequent and severe droughts, heatwaves and an elevated risk of wildfires. Reduced water availability may also threaten food security, disrupt ecosystems and spark social unrest as competition for this vital resource intensifies. |
Transition Risks
Transition risks stem from the shift to a low-carbon business model, including regulatory, technological, and market changes designed to meet climate change mitigation and adaptation objectives.
List of Transitional Risks
| Risk Category | Risk Subcategory | Risk Description |
| Transition Risks | Policy and Legal | The PAT scheme sets three-year energy-saving targets for energy-intensive industries like cement production, enabling the certification and trading of surplus savings, with financial penalties for non-compliance. Additionally, Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPO) mandate a minimum use of renewable energy, and future policies may introduce carbon pricing mechanisms, impacting operations and finances if targets are not met. |
| Technology | The limited commercial viability of low-carbon technologies like CCUS presents operational risks, as their implementation remains costly and in the developmental phase. Additionally, the evolving regulatory landscape and lack of clear commercial evidence create uncertainty, further complicating their adoption and impacting operations. | |
| Market | Although captive limestone mines ensure a secure raw material supply, rising costs of fuels like coal and coke pose financial risks. These fuel price increases are influenced by changing climate conditions, adding to the Company's operational vulnerabilities. |
Risk Mitigation
Based on the Company's climate risk assessment, none of its sites currently face physical climate risks. However, Ambuja Cements is implementing site-specific strategies to prepare for potential future scenarios and minimise the impact of unforeseen events on operations. These proactive measures incorporate adaptation strategies into existing operations, with a focus on short, medium, and long-term goals, ensuring that all future developments are designed to be both resilient and sustainable.
Internal Carbon Pricing
Ambuja Cements has introduced an Internal Carbon Pricing (ICP) mechanism, assigning a value of USD 28 per tonne of CO2 to promote sustainability and climate responsibility. This includes a shadow pricing model that evaluates financial risks at both site and organisational levels. The ICP helps Ambuja manage climate-related risks, reduce its carbon footprint, drive low-carbon investments and identify opportunities for sustainable growth.
Objectives of Implementing Internal Carbon Pricing
- Emissions Reduction
- Employee Engagement
- Carbon Planning
- Investment Decisions
- Supplier Selection
- Operational Efficiency
- Regulatory Compliance

Net Zero Commitment
Ambuja Cements is at the forefront of climate action and sustainability within its sector, with a strong commitment to contributing to India’s net-zero emissions goal. The Company aims to achieve Net Zero emissions by 2050, with its 2030 targets validated by SBTi. The Company is also aligned with the Global Cement and Concrete Association (GCCA) Roadmap for Net Zero Concrete by 2050.
The SBTi-validated targets can be viewed on the SBTi Target Dashboard.
Emission Reduction Targets 2030
Ambuja Cements tracks and reports carbon emissions across all sites in line with GHG protocols and accounting standards. The Company has committed to reducing its Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 21% per tonne of cementitious materials by 2030, using 2020 as the base year. Specifically, the Company aims to cut Scope 1 GHG emissions by 20% per tonne of cementitious material and Scope 2 GHG emissions by 43% per tonne over this period. This target includes biogenic emissions and removals from bioenergy feedstocks.
For more details, refer to Science Based Targets Dashboard
Ambuja Cements Limited has joined the Alliance for Industry Decarbonization (AFID) — a global coalition of companies working to accelerate the transition to Net Zero in alignment with the Paris Agreement. Ambuja is the first cement manufacturer worldwide to join AFID, a platform that fosters the exchange of insights and experiences among private and public stakeholders in energy-intensive sectors.
As part of its green energy strategy, the Company has outlined a plan to invest H 100 billion in renewable and green energy projects, including a 1 GW capacity and 376 MW from Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS). By FY 2027-28, Ambuja aims to power 60% of its expanded capacity with green energy, a move that will significantly reduce its carbon footprint while generating substantial economic benefits.
Cement Company to join AFID
Performance on SBTi Targets
| GHG Emissions | Scope 1 | Scope 2 |
| Target Year 2030 |
440 kg/tonne
Of cementitious material |
10 kg/tonne
Of cementitious Material |
| Performance in FY 2024-25 |
537 kg/tonne
Of cementitious Material |
17 kg/tonne
Of cementitious Material |
Decarbonisation Levers at Ambuja Cements
-
Higher Energy Efficiency
-
Increasing consumption of alternate fuels

-
Increase in Thermal Substitution Rate

-
Improved Technology

-
Optimising clinker factor
-
Alternate raw materials
-
Zero carbon heating technology

-
Innovation to optimise use of natural resources

-
Decarbonisation of Electricity
-
Use of renewable energy

-
Use of green energy Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS)
-
No new fossil fuel based captive power plants

-
Decarbonise Supply Chains
-
Supplier Engagement for reducing carbon footprint

-
Procurement Policy and Choices

-
Increasing rail and sea transport
-
Business Model Innovation
-
Increased sustainable marine and rail logistics

-
Usage of EVs


Future Initiatives
- Pilot on carbon capture and utilisation/storage
- Future-ready technologies like green hydrogen, carbon capture & utilisation
Towards Net Zero
Ambuja Cements is making significant progress toward its Net Zero goals by adopting zero-carbon heating technology to decarbonise its cement manufacturing process. The Company has formed a strategic partnership with Finland-based technology and engineering firm Coolbrook. Through this collaboration, Ambuja will implement Coolbrook’s proprietary RotoDynamic Heater™ (RDH™) technology, which will substantially reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
Energy Management
To drive continuous improvement, Ambuja Cements conduct regular energy audits to identify opportunities for enhancement and monitor progress against set targets. The Company’s operations are ISO 50001 certified, and it offers training programmes to employees to raise awareness on energy efficiency. This includes an in-house course on Energy and Emissions, available through its online platform, E-Vidyalaya-Percipio.com. By prioritising innovation and energy efficiency, Ambuja aims to reduce both thermal and electrical energy consumption while optimising energy costs. Through its research investments, the Company is on track to meet its goal of reducing energy consumption by 2030.
Energy Consumption
As a high energy consuming industry, cement manufacturing requires effective energy management to optimise costs and reduce environmental impact. Ambuja Cements monitors energy performance across all sites, reviewing key findings in monthly management meetings. The Company’s efforts are focused on improving energy efficiency, reducing consumption, and achieving cost savings. Ambuja Cements is also working to lower thermal and electricity use by harnessing renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, while efficiently utilising waste heat from its processes.

Enhancing the Energy Efficiency of Operations

Using Alternative
Fuels
(Co-processing)
Improving Thermal Substitution Rates
Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS)
Renewable Energy
Green Products
Total Energy Consumed in FY 2024-25
Thermal Energy
Energy consumed from renewable and green sources
Specific electrical energy consumption
Energy Efficiency
Ambuja Cements has consistently invested in reducing both thermal and electrical energy consumption per tonne of cement produced. Several of its plants are part of India’s Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) scheme, where specific thermal energy consumption has steadily decreased over time. The PAT scheme designates high-energy industries as consumers, requiring them to submit annual energy consumption reports and undergo mandatory energy audits. It sets energy consumption norms, verifies savings, issues energy savings certificates, and allows for the trading of these certificates. This has led to a reduction in energy use and carbon emissions, helping the Company move toward more sustainable operations.
Specific Electrical Energy Consumption
kWh/tonne of cement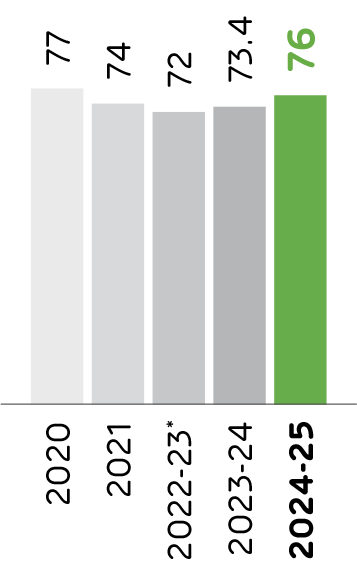
Specific Thermal Energy Consumption
(kCal/kg of clinker)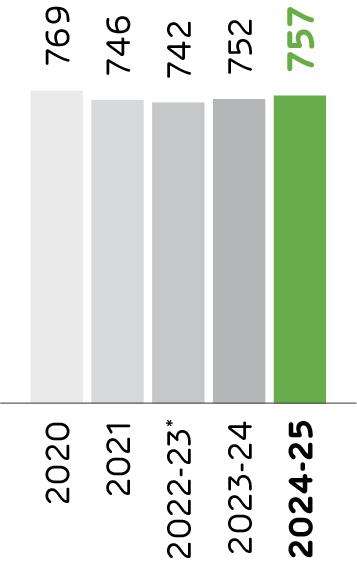

Renewable and Green Power
Ambuja Cements is investing significantly in renewable energy to reduce its carbon footprint and lessen reliance on conventional fossil fuel-based electricity. The Company aims to raise its share of green power to 60% by 2028 through INR 10,000 crore investments focusing on solar, wind energy, and Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS). This strategy supports Ambuja’s commitment to environmental sustainability, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and advancing clean energy practices. These initiatives align with a broader vision, positioning Ambuja Cements to lead the way in renewable energy within the cement sector.

*Note: The Company had changed its financial year ending from December 31 to March 31. FY 2022-23 was for 15 months (January 01, 2022 - March 31, 2023). Therefore, the data for FY 2023-24 and FY 2024-25 is not comparable with the figures for the 15 months year ended March 31, 2023.
Alternative Fuel Resource (AFR)
Ambuja Cements employs a sustainable approach to managing industrial, agricultural, and municipal waste through advanced co-processing technology. The Company operates pre-processing and co-processing facilities across India, each equipped with storage areas, feeding arrangements, and laboratories. These state-ofthe-art facilities optimise waste management, focusing on energy recovery and recycling. In line with its sustainability commitment, Ambuja is increasing investments to modernise and enhance these facilities.
Expert teams work with like-minded customers to increase the utilisation of waste in manufacturing.
The pre-processing facilities are crucial in converting heterogeneous waste into a homogeneous mix, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. With ongoing improvements to its waste management infrastructure, Ambuja Cements consumed 0.54 MMT of alternative fuels during the reporting period. The use of these wastes replace use of fossil fuels and prevent the wastes finding their way to dump sites causing negative environmental impacts. The use of alternate fuels further solidifying Company’s commitment to sustainable and responsible waste management practices.
Alternative Fuels Consumed
Waste co-processed*
lakhs tonnes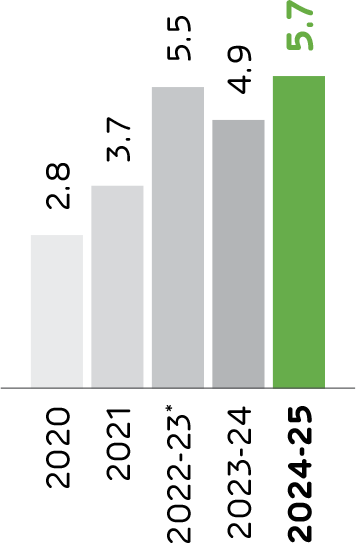
Geoclean: Leading the Way in Sustainable Waste Management
Ambuja Cements' waste management division, Geoclean, is revolutionising waste disposal by co processing municipal, industrial and agro wastes. This prevents dumping of wastes to environment and minimises environmental impacts from waste dumping. By harnessing co-processing technology, Geoclean enables resource recovery, reducing landfill waste and minimising environmental impact. With 5 pre-processing and 6 coprocessing facilities, Geoclean boosted its Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) to 9% in FY 2024-25.
Sustainable waste management plays a key role in supporting the Company's broader sustainability and carbon reduction objectives. Partnering with over 50 municipalities and various industries, Geoclean diverts waste from landfills, remediating more than 20 legacy sites and reclaiming over 200 acres.
In FY 2024-25, Geoclean co-processed more than 0.57 MMT of waste. As it continues to grow, Geoclean aims to achieve a 23% TSR by 2030, reinforcing its leadership in circular economy-driven waste management.

Thermal Substitution Rate
The Thermal Substitution Rates are increasing over the years and Ambuja Cements has a target to reach 23% by 2030, underscoring the Company’s commitment to sustainable waste management and reduced reliance on traditional fuels. Increasing the Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) involves replacing traditional fossil fuels with alternative energy sources like biomass and industrial waste. This shift not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions, but also decreases reliance on non-renewable resources, leading to potential cost savings. Additionally, utilising waste materials such as Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) as fuel supports waste management efforts by diverting them from landfills, thereby promoting a circular economy. In 2024, the Company inaugurated a pre-processing and co-processing facility at its Marwar plant in Rajasthan, capable of converting 220,000 tonnes of refuse annually into alternative fuel. This initiative is set to elevate the plant's TSR to 15%.
Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR)
Thermal Substitution Rate
(in %)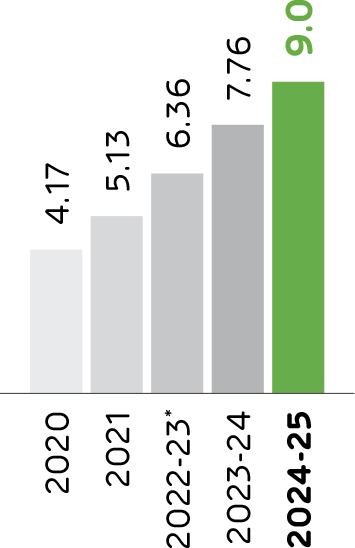


Green Products
Ambuja Cements is a leader in producing and selling blended cement with a significantly lower clinker factor, making it a more environmentally friendly option. By utilising materials like slag, waste gypsum and fly-ash, these products not only help reduce environmental impact but also contribute to building durable and resilient structures for the nation. Over 78% of the Company's production consists of blended cements. Ambuja’s green products are certified by GRIHA (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment), India’s national green rating system, underscoring their commitment to sustainable building practices.
Clinker Factor
Blended Cement
Managing Air Emissions
Ambuja Cements actively manages air pollution by addressing key sources and implementing effective control measures:
- Fuel Combustion: Generates nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur oxides (SOx), contributing to environmental impact.
- Particulate Emissions: Produced from fuel combustion and vehicle movement within operations.
Control Measures:
- Electrostatic Precipitators and Bag Filters: Manage flue and process emissions effectively.
- Closed Conveyor Belts: Minimise dust generation during material transfer.
- Dust Suppression: Includes water sprinkling, tyre washing and other measures to control dust.
- Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS): Track SOx, NOx, dust/particulate matter and other emissions at all plants.
- Digital Display: Real-time emissions data displayed at all monitoring locations across facilities.
NOx Emissions
SOx Emissions
Dust Emissions
Water Management
Ambuja Cements has long been a pioneer in sustainable water management, achieving and maintaining a Water Positive status for over a decade. The Company goes beyond compliance, setting benchmarks in water conservation, efficiency, and community impact. Through large-scale rainwater harvesting, watershed development, and innovative recycling systems, Ambuja not only reduces its freshwater footprint but also enhances local water security.
Ambuja Cements has implemented a comprehensive water stewardship policy, prioritising the protection and conservation of water resources. Central to this approach is the continuous monitoring and measurement of critical water-related factors, including withdrawal, consumption, recycling, and disposal. The Company has set ambitious goals to maintain its water-positive status, achieving a remarkable 12x surplus over its annual water consumption. This commitment not only ensures sustainable operations but also contributes significantly to water security in the communities where it operates.
Objectives of Water Stewardship Framework
Reduce Dependency on Freshwater
Seek to minimise reliance on freshwater resources for operations
Ensure Water Security
Ensure water security for communities residing beyond their immediate boundaries
Become Water Positive
Aim to continue being water-positive through sustainable water management practices
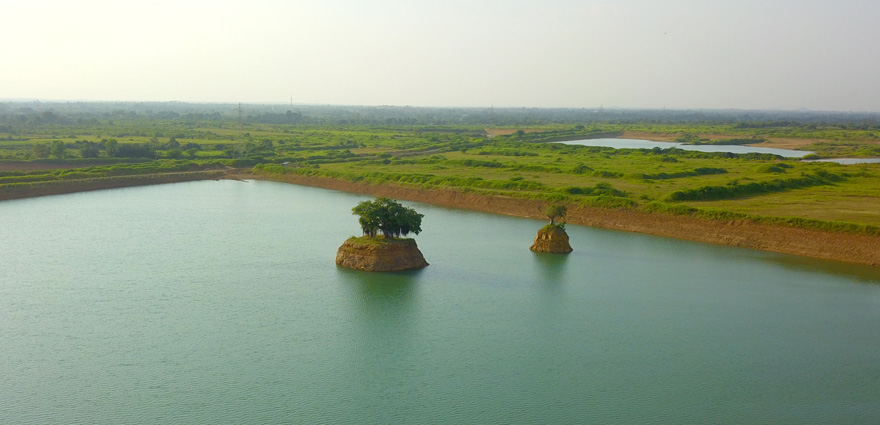

Wastewater Discharged
Recycled water used in cement manufacturing
Freshwater consumption from Harvested Rainwater
Water Positive
Water Withdrawal and Consumption
Ambuja Cements recognises the critical importance of responsible water use across all its operations. The Company continuously evaluates and refines its water withdrawal processes to minimise impact on shared resources. Key enablers include:
- Efficient Resource Use: Rigorous monitoring and implementation of best practices to ensure water is used judiciously and efficiently
- Transparency in Reporting: Maintaining clear, comprehensive reporting on water consumption, aligning with industry standards
- Alignment with Industry Practices: Emphasises water stewardship, reduction in freshwater withdrawals, and transparent communication of its water management strategies
Fresh Water Consumption in Production
Operations in Water Stressed Areas
A few of the Company’s plants (Maratha, Rabriyawas, Ropar, Dadri) are situated in water-stressed regions, making efficient water management crucial. Despite these challenges, the Company meets all regulatory requirements and works to minimise its impact on local water resources and maximise use of harvested rain water and recycled water.
Water Intensity
Ambuja Cements has set an ambitious goal to reduce the intensity of freshwater usage per tonne of cement produced. Over the years, the Company has made significant improvements in water intensity and is on track to achieve the target of reducing gross water intensity per tonne of cement produced by 10%, and is taking all initiatives to achieve this. These achievements reflect its commitment to water efficiency and responsible resource management.
In line with industry best practices, Ambuja Cements ensures transparent progress reporting and sets clear, measurable goals as part of its Sustainable Development Plan for 2030. Notably, the Company has already surpassed its target to become 10x water positive by 2030, reaching to 12x water positive for the reporting year. This marks the Company's dedication towards continuous enhancement of its operational practices.
Consumed Per Tonne of Cementitious Material
Gross Water Positive
Wastewater Recycling and Reuse
Ambuja Cements has established robust wastewater recycling and reuse practices across its operations, in line with industry best practices. These initiatives are designed to maximise water efficiency, significantly reduce dependence on freshwater sources, and lower the overall water footprint. By implementing advanced recycling systems, Ambuja Cements effectively repurposes treated wastewater for applications such as dust suppression and landscaping, further underscoring its commitment to sustainable water management and environmental stewardship.
Recycled water used in cement manufacturing
Wastewater Discharge
Ambuja Cements ensures that all wastewater generated at its plants is rigorously treated and recycled for applications such as gardening and dust suppression, achieving zero discharge beyond its premises. By adhering to industry best practices, the company effectively minimises its water footprint while promoting sustainable resource management.
Wastewater Discharged
Rainwater Harvesting and Conservation
The Company actively collaborates with developers, governments and communities to promote water conservation practices aligned with its water management strategy. Initiatives include utilising closed mine pits for rainwater harvesting and groundwater recharge, reviving village ponds with rural communities, partnering with governments on projects like check dams, engaging developers for rainwater harvesting, implementing modular zero water curing solutions and undertaking rainwater harvesting across communities to ensure drinking water security.
Waste Management and Circular Economy
Ambuja Cements is committed to the sustainable consumption of resources, minimising waste generation, and adhering to the principles of a circular economy. The Company prioritises effective waste management by implementing industry best practices and exceeding regulatory requirements. Ambuja aims to reduce the negative impacts of improper waste handling by ensuring full compliance with relevant environmental laws.
Waste minimisation and recycling are integral components of Ambuja Cements’ sustainability strategy. A significant portion of waste-derived resources is utilised, reducing the need for mined materials and preventing harmful environmental disposal. The Company conducts regular waste audits to identify areas for improvement and implement action plans for waste reduction. Ambuja has set ambitious targets and continues to invest in minimising waste generation. With a strong commitment to sustainability, Ambuja sends zero waste to landfills and organises regular employee training to promote responsible waste management practices and foster a culture of environmental stewardship.
Waste Generation
Through advanced waste management practices, the Company has significantly reduced waste generation. Following types of wastes are generated by the Company:
- Plastic Waste
- E-waste
- Bio-medical Waste
- Construction and Demolition Waste
- Battery Waste
- Other Hazardous Waste
- Non-hazardous Waste
The Company is committed to effective waste collection and segregation at the source, classifying materials as hazardous or non-hazardous and storing them in designated areas.
Total Waste Generated
For more details of waste generation, please refer to BRSR, Principle 6, Question 9.
Waste Management
The Company focuses on recycling and co-processing of waste. Some of the initiatives on waste management are:
- Plastic waste is mainly disposed through in-house co-processing and a minimal quantity such as burst bags are dispposed through authorised scrap dealers
- Bio-medical waste is disposed through incineration at
- E-waste is recycled through authorised recyclers
- Hazardous waste (used oil, discarded drums) is reused at plant or is co-processed in cement kiln and the quantity which cannot be co-processed is sent to common authorised facility
- Scrap is sold to authorised vendors
- Mining overburden is repurposed and used for backfilling within the mines
Waste Disposal
E-waste, biomedical waste, scrap and similar materials are responsibly disposed of through authorised recyclers accredited by regulatory bodies. At many of its plants, plastic waste and used oil are co-processed in cement kilns, preventing landfill disposal. Wastes like fly-ash are recycled into manufacturing of blended cement.
Hazardous Waste Sent to Landfill
Waste Derived Resources
During the year, Ambuja utilised 20.88 million tonnes of wastederived resources. This includes 0.57 million tonnes of alternate fuels and 8.1 million tonnes of waste derived raw materials like fly-ash, gypsum and slag. Ambuja has maintained cement quality while conserving resources and advancing its sustainability goals.
of Waste-derived Resources Utilised

Biodiversity Management
Biodiversity management is a key focus in the Company's materiality assessment, acknowledging the role of healthy ecosystems in mitigating natural disasters. Robust biodiversity enhances essential ecological services vital for businesses and society. ACL's comprehensive biodiversity policy addresses operational impacts by guiding the identification and evaluation of biodiversity-related risks across project sites and implement a mitigation hierarchy of avoid, minimise, restore and offset and measure progress on regular basis. The policy is applicable to all operations and to suppliers and value chain partners.
The policy aims to No Net Deforestation through time-bound afforestation programmes. It aims to achieve No Net Loss of Biodiversity in all operations and at sites where critical habitat is present with an ultimate objective of achieving Net Positive Gain of biodiversity.

Ambuja Cements has undertaken a comprehensive Nature Risk Assessment, including a Biodiversity Risk Assessment, based on the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) LEAP approach. This methodology facilitates the identification, evaluation, and reporting of nature-related impacts and dependencies. TNFD defines dependencies as ecosystem services essential for business operations, such as a clean and consistent water supply. Businesses also have impacts—both positive and negative—on environmental assets and ecosystem services.
These dependencies and impacts create potential risks for organisations. Physical risks may arise due to climatic (e.g. extreme weather events) or geological (e.g. seismic activity) factors, or through shifts in ecosystem equilibrium, such as soil degradation or marine ecology changes. These risks may be acute (event-driven), chronic, or both. Transition risks stem from an organisation’s misalignment with evolving regulatory and policy landscapes.
Nature-related opportunities are defined as activities that deliver positive outcomes for businesses and ecosystems by mitigating negative impacts or contributing to environmental restoration. Cement production has a significant dependency on natural capital, particularly abiotic resources such as minerals (e.g. limestone) and water. Indirectly, the industry relies on ecosystem regulation services, including climate and water regulation, as well as protection against floods and storms. However, mining activities required for raw material extraction result in land use changes, affecting flora and fauna.
Risk Assessment
Ambuja Cements conducted a detailed mapping of its operations within a 10 km radius of each site to assess potential impacts and dependencies on biodiversity and ecosystem services. The IBBI Ecosystem Services Matrix tool was utilised for ecosystem service mapping, and risk identification was aligned with global standards, including the International Finance Corporation Performance Standard 6, the UN Convention on Biological Diversity’s Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework, the Dow Jones Sustainability Index (DJSI) and the TNFD Framework. Additional tools such as DOPA, eBird India and Global Mangrove Watch were also employed.
Following this assessment, a risk categorisation matrix was developed for each site, evaluating impact and dependency. The study identified sites as high-risk, medium-risk, or low-risk, requiring varying levels of intervention to mitigate biodiversity-related risks. While none of Ambuja Cements' sites were classified as high-risk, the Nalagarh and Sankraila Ropar sites were identified as medium-risk.
Biodiversity Action Plan
In response to the identified biodiversity risks, Ambuja Cements has developed a comprehensive Biodiversity Action Plan (BAP) that integrates nature-based solutions and aligns with the IUCN Mitigation Hierarchy. The BAP includes site-specific action plans, such as greenbelt development, wildlife monitoring around plants, construction of rainwater harvesting structures and mangrove restoration initiatives. These measures reflect the Company's commitment to mitigating environmental risks and fostering ecological sustainability.
Biodiversity Mitigation Hierarchy
| Avoid | Reduce | Regenerate & Restore | Transform |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implementing measures to prevent adverse impacts on biodiversity from the outset. | Reducing unavoidable improved management impacts through practices and technologies. | Rehabilitating affected ecosystems to restore their functions and services. | Actions to achieve No Net Deforestation and No Net loss to Biodiversity and progress towards Net positive. |
| E.g. Greenbelt Management: Adhering to CPCB guidelines by using native tree species and avoiding monoculture plantations to enhance biodiversity and mitigate pollution. |
E.g. Lighting
Management: Re-orienting
lighting systems to
reduce impacts on
nocturnal wildlife.
E.g. Compensatory tree plantations in case of trees cut during expansion. |
E.g. Rainwater Harvesting: Developing structures to increase groundwater recharge and restore local water bodies; Mangrove Restoration. | E.g. Targets to plant trees at each site and working with communities around. |
Biodiversity Protection and Enhancement Measures
Ambuja Cements strictly adheres to Indian environmental laws and regulations, including the Forest Conservation Act and the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) Act, ensuring compliance with the principle of No Net Deforestation. Under the Forest Conservation Act, 1980, and the Compensatory Fund Act, 2016, the Company is committed to offsetting any deforested land used for operational activities through afforestation. Additionally, a comprehensive Mine Closure Plan is in place at all mining locations, incorporating compensatory afforestation and site rehabilitation at the time of closure. The Company also complies with the Green Belt Development guidelines set by the Government of India.

To further prevent environmental degradation and enhance biodiversity, Ambuja Cements has implemented several key initiatives:
- Community Collaboration: The Company actively engages with local communities to manage afforested and rehabilitated areas while partnering with them to oversee adjoining offset zones.
- Tree Plantation Targets: As part of the Adani portfolio of companies, Ambuja Cements is committed to planting 8.3 million trees by 2030, with 6.6 million already planted.*
- Enhancing Degraded Habitats: Targeted habitat management plans are being implemented to restore and enhance degraded ecosystems across operational sites.
- Responsible Waste Disposal: Overburden and waste materials are systematically disposed of in designated non-mineralised zones, following an approved Mine Plan. Progressive mine closure strategies are in place at all locations as per statutory requirements.
- Daytime Operations: In proximity to protected areas, mining operations and raw material transportation are restricted to daylight hours to reduce environmental impact.
- Spillage Prevention: Mine tippers are equipped with advanced multi-cap covering systems to prevent material spillage during transportation.
- Capacity and Awareness Building: Continuous training initiatives are conducted for employees and local communities to minimise biodiversity impact, with regular awareness sessions for all stakeholders.
*Consolidated

IBBI Membership
Ambuja Cements Limited is a proud member of the India Business and Biodiversity Initiative (IBBI). As a national platform for businesses and stakeholders, IBBI fosters dialogue, knowledge sharing and collaborative learning to integrate sustainable biodiversity management into corporate practices. Through this membership, Ambuja Cements reinforces its commitment to environmental stewardship by aligning its operations with biodiversity conservation principles, ensuring long-term ecological balance while driving responsible business growth.
A Celebration of Biodiversity on World Environment Day 2024
On World Environment Day 2024, Ambuja Cements launched a distinctive initiative to raise environmental awareness and celebrate biodiversity. The centrepiece was an engaging photo campaign with a unique twist: participants were encouraged to capture images of local flora and fauna, sharing them along with their scientific names, highlighting the beauty and complexity of nature. In addition, cement plants organised sapling planting drives and creative competitions, inspiring both team members and their families to take active roles in environmental conservation.
These activities emphasised the critical importance of biodiversity protection and hands-on participation. Through this personalised approach to conservation, Ambuja Cements sparked a sense of urgency, motivating action and a renewed commitment to preserving the natural world, thus fostering a culture of environmental stewardship for a sustainable future.

#GreenGems Campaign
Ambuja Cements marked World Nature Conservation Day 2024 with the launch of the #GreenGems Campaign, inviting employees to share images of local flora and fauna. With 51 entries, the campaign highlighted the team’s connection to nature and reinforced the Company’s commitment to sustainability.
The initiative reflects Ambuja Cements' dedication to its Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) goals, emphasising the importance of conserving the environment. Each photo shared echoed the Company’s pledge: NURTURE NATURE FOR A SUSTAINABLE FUTURE.
The success of the campaign underscores the collective effort to integrate sustainability into every aspect of the business, reinforcing Ambuja Cements’ commitment to a greener, more sustainable future.

Responsible Mining
Ambuja Cements adopts responsible mining practices that prioritise environmental protection and biodiversity conservation. The Company sources limestone from captive mines near its integrated plants, utilising sustainable extraction methods and innovative operational techniques. These mines are government-leased, thereby eliminating the need for resettlement and rehabilitation (R&R). At the Ambujanagar site in Gujarat, an eco-friendly, blast-free surface mining technique is employed to significantly reduce noise and dust pollution. At other locations, controlled blasting using high-precision electronic detonators is implemented to enhance safety and minimise environmental impact. The Company also utilises advanced mining technologies to conserve minerals, incorporating dust-suppression measures during drilling and maintaining haul roads to further reduce emissions. Covered conveyor belts are used to transport mined material securely and efficiently. Additionally, strict adherence to health and safety protocols is maintained at all sites, while green belts around mines and plants help mitigate dust pollution and safeguard local biodiversity. Ambuja Cements also invests in training its team members to work collaboratively with local communities, further minimising the ecological footprint of its mining operations.

Regulatory Compliance
Ambuja Cements is committed to upholding responsible and sustainable business practices by adhering to a comprehensive range of environmental regulations across its operations. The Company ensures that all necessary permissions and approvals are secured to meet these regulatory obligations. To efficiently monitor and manage compliance, Ambuja Cements employs the Legatrix software system, an IT-enabled legal support service that provides real-time visibility and in-depth coverage of legal and regulatory compliances. Key environmental regulations pertinent to its operations include:
- Environmental Clearances and EIA Notification, 2006
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
- Noise Pollution (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000
- The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- Hazardous and Other Wastes (Management & Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2016
- Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016
- Bio Medical Waste Rules, 2016
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016
- E-Waste Rules, 2016
- The Construction and Demolition Waste Management Rules, 2016
Beyond mere compliance, Ambuja Cements strives to set industry benchmarks by excelling in sustainability practices and promoting exemplary environmental stewardship. This commitment is reflected in the Company's proactive approach to environmental management and its dedication to continuous improvement in sustainability performance.