We are fully aware of the potential environmental and social consequences of our operations. Acknowledging our responsibility, we actively strive to advance sustainable development and mitigate climate change. To achieve this, we have implemented rigorous measures to ensure our manufacturing processes are environmentally responsible with the help of careful resource allocation, energy-saving initiatives, and efficient waste management, prioritising sustainable practices. We leverage technology to reduce our carbon footprint along with increased usage of waste derived resources and creating a portfolio of green products.

Stakeholders impacted

Dealers

Suppliers

Employees
Community
and NGO

Government and
regulatory authorities
Material issues addressed
- Biodiversity
- Sourcing of water
- Land acquisition for mines and new operations
- Relocation and rehabilitation (post mine closure)
- Circular economy
- CSR
- Sustainable supply chain
- Compliance with regulatory requirements
- Customer satisfaction
- Energy efficiency
- GHG emissions and climate change
- Other air emissions
- Waste management
Key risks addressed
- Environment and sustainability
SDGs impacted

Capital-wise performance > Natural capital
Overview
We continue to invest in improving our environmental performance, which results in significant cost savings.
No significant fines or penalties (>$10,000) were incurred during the reporting period. No formal grievance about environmental impact had been filed through the various grievance mechanisms during the reporting period. Through our advocacy and action, we intend to ensure that climate change measures are integrated into national policies, strategies, and planning.
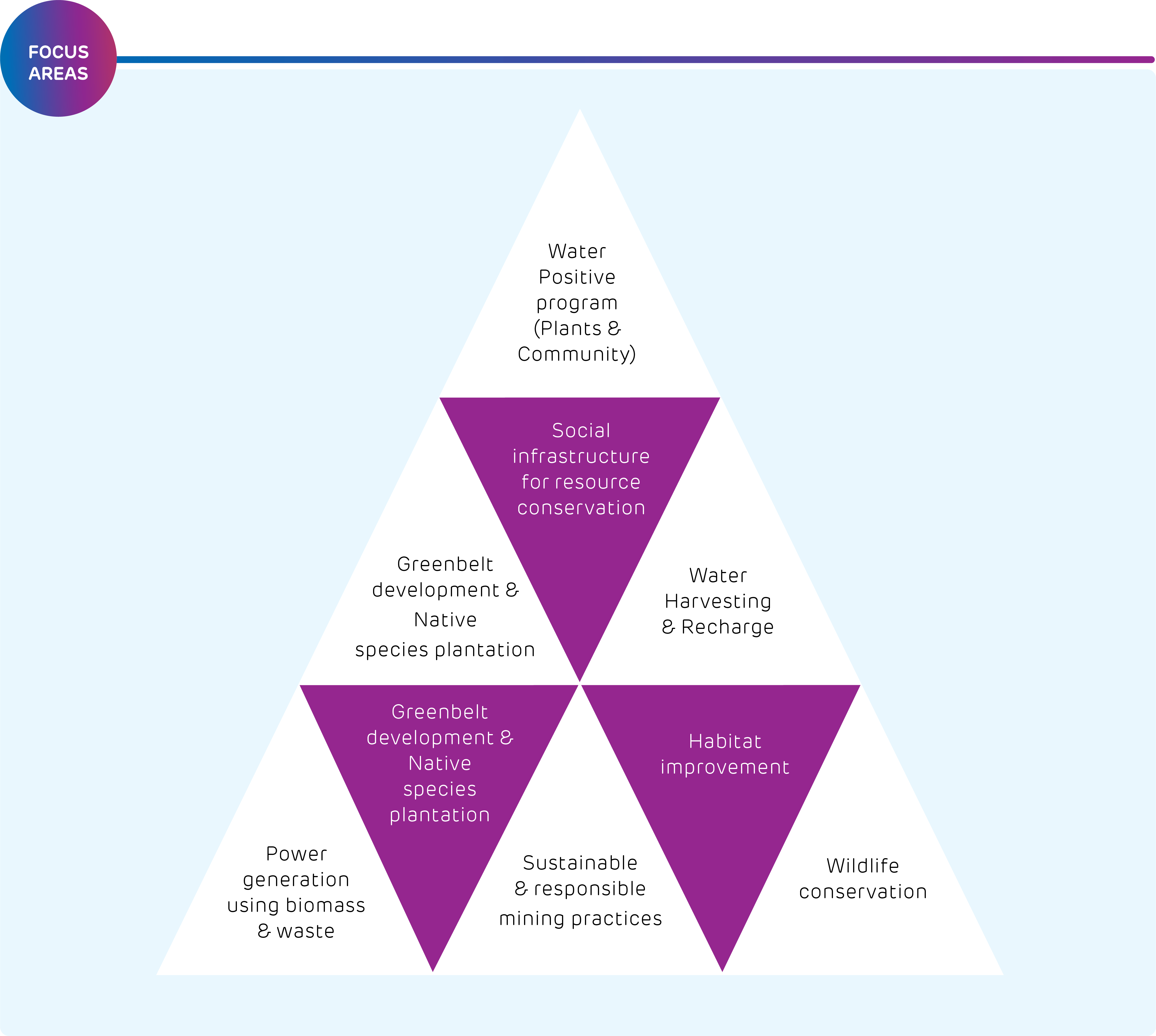
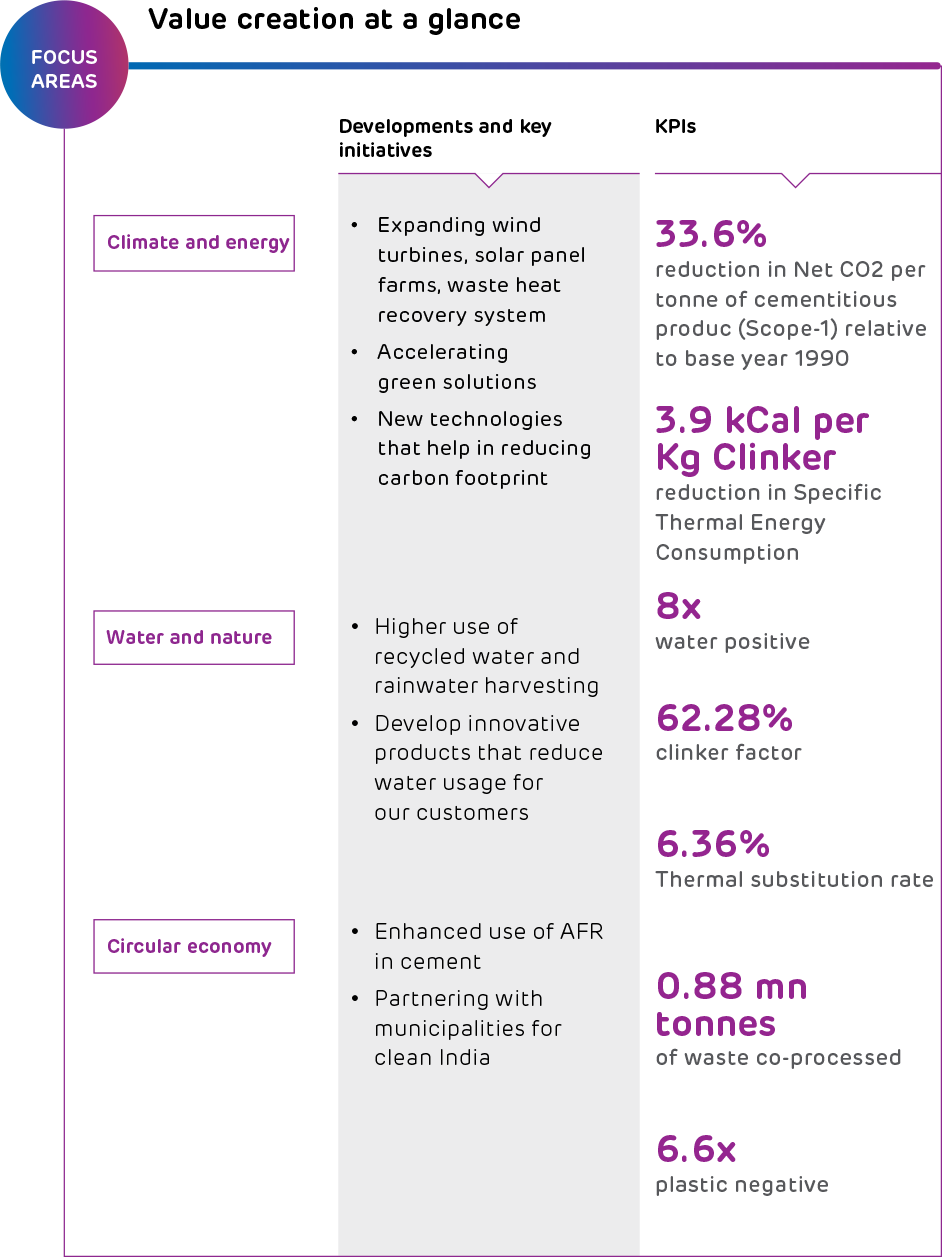
Climate and Energy
Carbon emission
Aware of the cement industry’s contribution in GHG emissions globally, we have undertaken a four-pronged strategy to reduce our carbon emission:
Use of alternative materials to reduce clinker factor
Improve energy efficiency (thermal and electrical) and process technology
Arrested from being released into the atmosphere during the reporting period
Waste heat recovery and use of Renewable Energy (RE)
Optimise fuel composition, along with the use of waste as alternative fuel

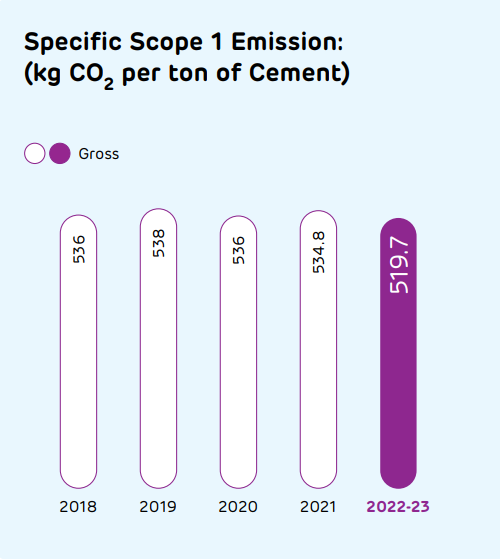
In alignment with World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) Cement Sustainability Initiative (CSI) CO2 protocol, we monitor and report our emissions from all manufacturing locations. We disclose our environmental performance as per CSI and GRI guidelines and annually in the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) and Dow Jones Sustainability Index (DJSI).
Our Scope 1 emissions include direct emissions from owned or controlled sources, including emissions due to fuel combustion in kilns or from onsite energy generation and clinker production. Scope 2 emissions are associated with purchased electricity from grid. Scope 3 emissions include other indirect GHG emissions, including emissions from purchased products and services, fuel and energy-related activities, upstream and downstream transportation and distribution, waste generated in operations, business travel and employee commuting among others.
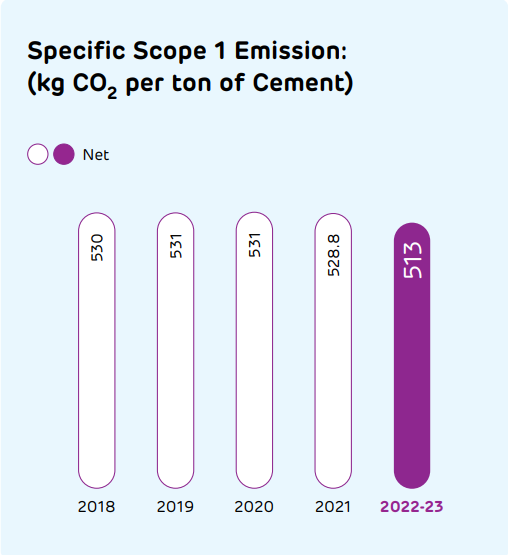
Capital-wise performance > Natural capital
Other emissions
Our manufacturing process does not emit any ozone depleting substance (ODS). The ODS data covers only core processes and not the administrative facilities, which include office buildings, staff quarters among others at plants and offices. The installed continuous monitoring systems across our plants help us monitor NOx, dust/particulate matter and any other significant emissions from our nine kilns or raw mill stacks. Real time display of these data, except for data on captive power plants and other stacks, is made available on the website of the regulatory agencies. Further, we have invested in Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction (SNCR) systems, new Electro-Static Precipitators (ESPs) and baghouse modifications, reinforcing our commitment towards emission minimisation.
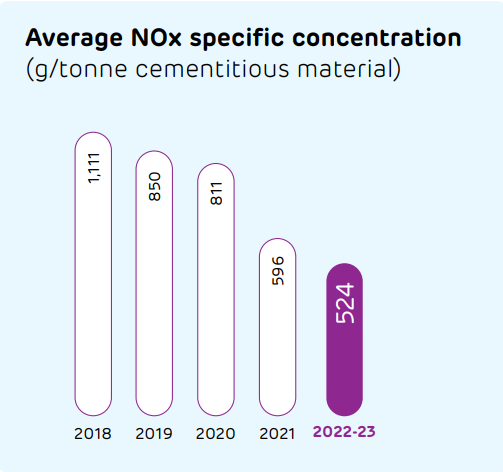
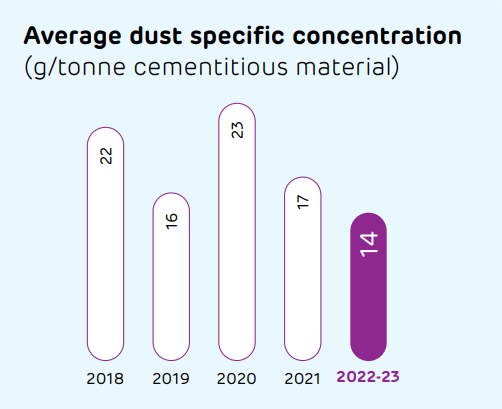
Energy management
We are undertaking measures to reduce our energy intensity across the cement value chain and have implemented ISO 50001:2011 standards to augment our energy management system. We are working relentlessly to increase the share of renewables such as solar, biomass, and wind in the energy mix. We are using alternative fuel and raw material (AFR) and waste heat recovery to increase our energy efficiency. We use waste derived raw materials like fly ash, slag, and waste gypsum etc. in our manufacturing process, which has resulted in lower clinker factor. We have also optimised our processes for use of low-grade limestone and waste derived alternative fuels. We are proud to have set new benchmarks in the industry in energy use.
Performance during the reporting period
As a percentage of total operating cost, energy cost stood at 36%. About 58% of our power requirements are met through captive energy sources.

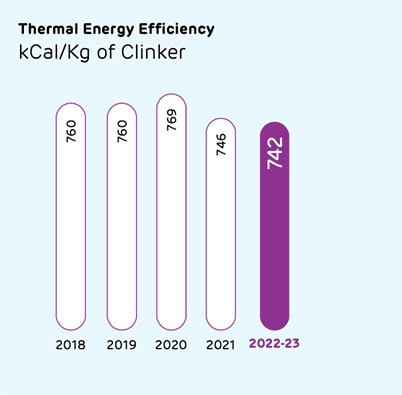
A detailed list of various energy efficiency measures taken are listed in the Performance table (Page 377), and also available on ambujacement.com/investors/ annual-reports.
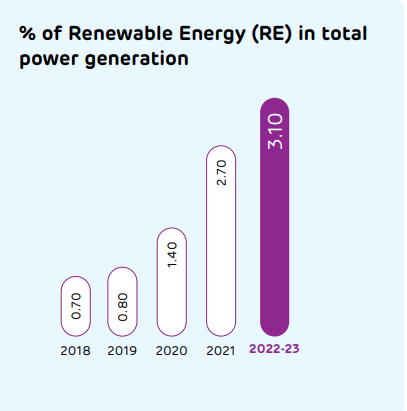
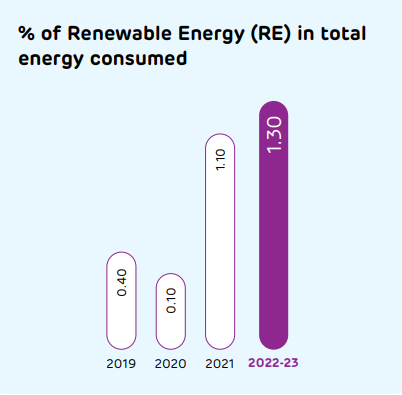
Renewable energy
Renewable energy remains a key factor for reducing our carbon footprint.
We use biomass at the captive power plants as well. Along with renewable energy certificates, the power cost optimisation strategy also helps us add value to power sourcing and be compliant in renewable purchase obligations.
Capital-wise performance > Natural capital
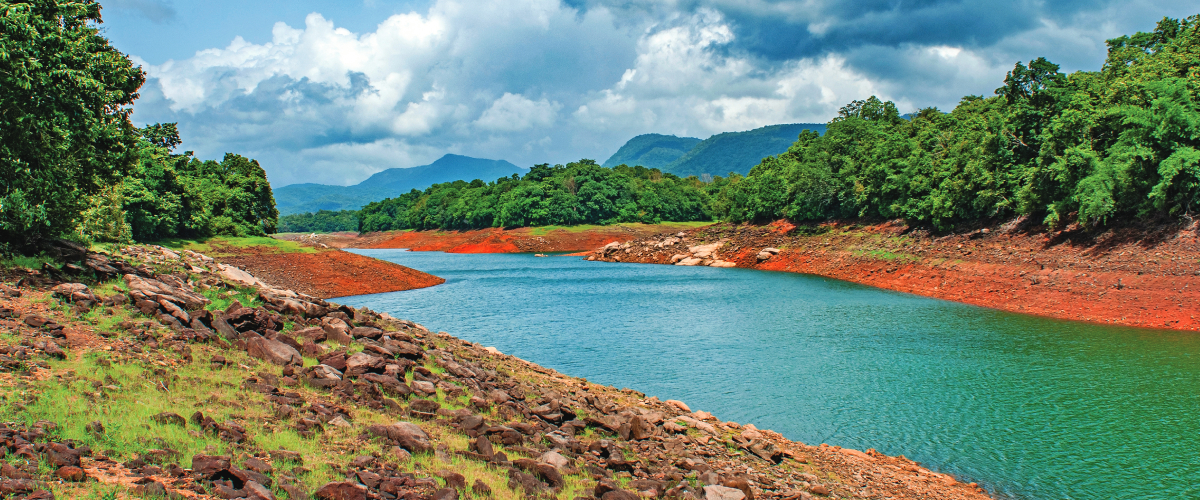
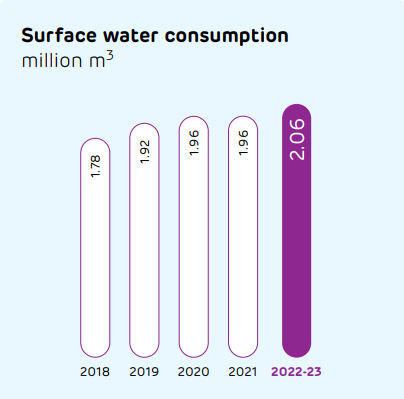
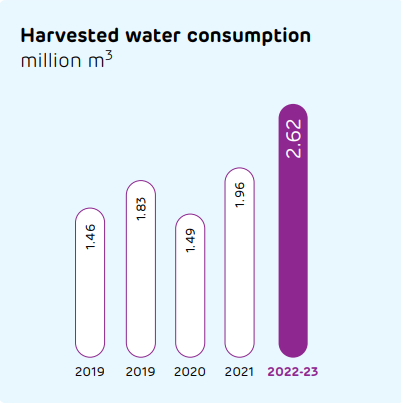
Water and nature
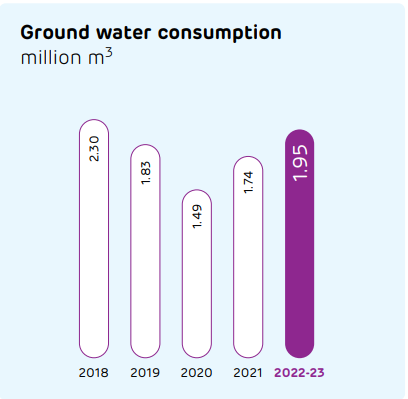
Water is among the key pillars of our Sustainable Development Plan 2030. Our dry process of cement production requires significantly less water than other processes. And now, our products are helping minimise the use of water in construction. Our steadfast efforts in ensuring water efficiency enabled us to turn 8x water-positive.
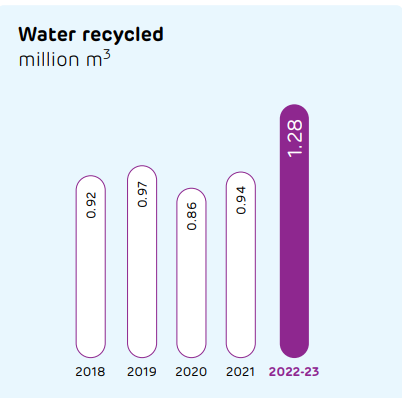
Despite having five of our plants are in water scarce regions, we comply with all water-related regulatory requirements. At our plants, we are maximising the use of recycled water that has been treated at our effluent treatment plants as well as reverse osmosis plants. Recycled water is also used for dust suppression and gardening, along with other purposes.
At the community level, we have undertaken water conservation and rainwater harvesting projects under the aegis of our CSR arm (Details can be found on page 60 of this report).
Performance during the reporting period
Our water sustainability risk assessment framework has been developed in association with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). It considers business/company risks as well as the basin risk, covering various risk aspects and identifying units with water stress.
This assessment also uses the WBCSD Global Water Tool. Scenario analysis to identify the potential impact on operations has also been conducted.

Biodiversity management
Our biodiversity policy is enshrined in the Group’s Quarry Rehabilitation and Biodiversity Directive. We adhere to Indian national regulations and are a signatory to the India Business and Biodiversity Initiative (IBBI) of the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), and Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ).
As part of our Sustainable Development agenda, we are committed to achieving ‘Positive Change in Biodiversity’ (net positive impact) by 2030. For all our sites, we carefully classify our ecological assets and maintain a biodiversity inventory. We also assess the net positive impact through set KPIs every three years. We have implemented a new baseline biodiversity assessment at our sites through a Biodiversity Indicator and Reporting System (BIRS) developed by experts from the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). BIRS assessments were conducted in 2017, 2019 and 2020.

We are in the process of implementing mitigation hierarchy for our biodiversity management and conservation efforts which includes three key elements: avoid, minimise and restore. We avoid undertaking operations near any of the World Heritage Sites and IUCN Category I-IV protected areas. Our operating sites are not located adjacent to indigenous peoples’ territories.
We plant trees on the overburden and area around the mines and on the mine lease boundaries, which helps us reduce dust pollution and promote the absorption of carbon emissions and preservation of regional biodiversity. We regularly train our team members working closely with communities to ensure minimal impact on the biodiversity. Our overburden/interburden or waste material is disposed of separately in nonmineralised zones through an excavator-dumperdozer combination as per the approved mine plan. Progressive mine closure plans are available as per statute for all locations.
Capital-wise performance > Natural capital
BIRS score (Site Biodiversity Index on a scale of 1-4)
| Units | 2019-20 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| Ambujanagar, Gujarat | 1.9 | 1.7 |
| Darlaghat, Himachal Pradesh | 2.1 | 2.1 |
| Rabriyawas, Rajasthan | 2.3 | 2.1 |
| Maratha Cement Works, Maharashtra | 2.1 | 2.0 |
| Bhatapara, Chhattisgarh | 1.9 | 1.7 |
Protected areas
Protected areas like the Majathal Sanctuary and Darlaghat Conservation Reserve (both in Himachal Pradesh) are situated within 10 km of our mining/ plant operations at Darlaghat. The Gir sanctuary lies within 10 km of a mining site at Ambujanagar, Gujarat. We have prepared a wildlife conservation plan for key species, approved by the state government, for Darlaghat. Biodiversity Action Plan (BAP) for all our five plants with mining sites is being implemented.
We continuously monitor biodiversity and set protection and action priorities for species like IUCN red data list and regional threatened species list. We conduct periodic ecological study on species and habitats through our local partners such as the Gujarat Institute of Desert Ecology (GUIDE), university experts and research institutions to identify the causes of decline in species and take corrective measures.
Key aspects of our biodiversity management
Partnering with local experts and forest department to develop comprehensive biodiversity action plans with regional measurable targets across sites, and act on the outcomes of our assessment
- Improving degraded habitats across sites through targeted habitat management plans
- Working closely with the community to adequately manage the planted and rehabilitated areas and partnering for the management of any other adjoining offset areas
- Turning regenerated areas into natural habitats by adopting new forestry practices
- Carrying out mining operations and raw material transportation only during the daytime near protected areas
- Providing mine tippers with a multi-cap covering system to avoid spillage of material during transportation
Promoting a circular economy
Through Geoclean, the waste management arm of Ambuja Cement, we have emerged as a pioneer in the industry in effectively co-processing waste in the cement kiln .
It has 4 dedicated pre-processing facilities with installations for blending liquids, shredding solids and sludge, and homogenising waste before it is coprocessed sustainably at six locations. As Geoclean, we co-process waste from industries and municipalities in our kilns as alternative fuel. This reduces the use of traditional fuel, which, in turn, results in natural resource conservation and GHG mitigation, contributing towards a circular economy. Geoclean has developed 6 pre-processing and 13 co-processing facilities with storage areas, feeding arrangements, and laboratories across India, that support both ACC and Ambuja Cement. During the reporting period, we co-processed ~0.54 million tonnes of alternative fuels, substituting 6.36% of total thermal energy.