Stakeholders Impacted
Communities and NGOs
Government and Regulatory Authorities
Suppliers
Channel Partners
Employees
Material Topics
- Climate and Energy
- Air Quality
- Water Management
- Circular Economy
- Biodiversity
- Sustainable Construction
Focus Areas
Developments and Key Initiatives |
Key Performance Indicators |
|
|---|---|---|
Net Zero |
On track to reach net zero by 2050 |
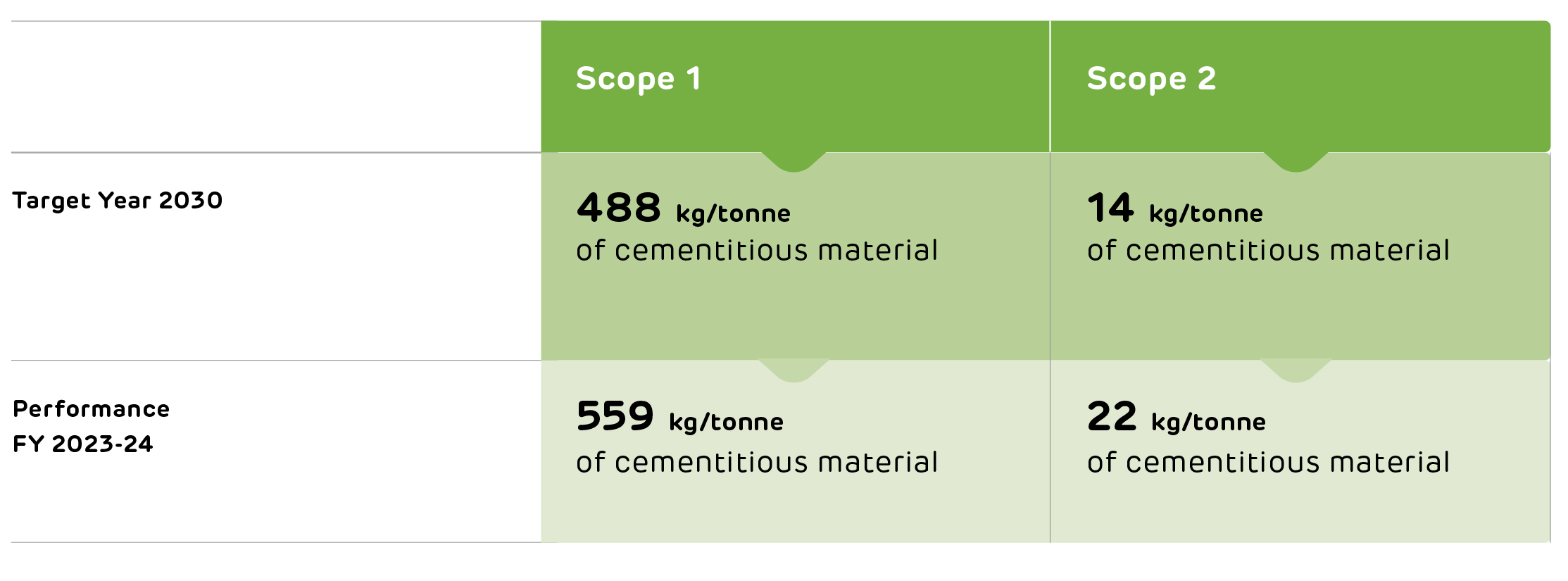
559 kg/tonne
CO2 Scope 1 emissions 22 kg/tonne
CO2 Scope 2 emissions |
Energy Efficiency |
Commissioned wind turbines, solar panel farms, waste heat recovery system Adopted newer technologies to reduce carbon footprint |
752 kCal/kg of clinker
Specific thermal energy consumption 7.76%
Thermal Substitution Rate |
Water Positivity |
Increased recycled water and rainwater harvesting usage Developed innovative products that reduces water usage for the customers |
11x
Water-positive |
Waste Management and Circular Economy |
Enhanced use of alternative fuels and raw materials in cement Adopted waste disposal initiatives under Geoclean Adopted initiatives to curb plastic waste through co-processing initiatives |
8.6 MMT
Waste co-processed 8x
Plastic negative |
Biodiversity |
On track to grow 2.42 million trees by 2030 |
1.05 lakhs (1.4 million till date)
Trees planted |
Sustainability Strategy
Ambuja Cements continues to set industry benchmarks in various sustainable practices. The Company has a set of policies to guide its actions. The Company’s corporate responsibility committee, comprising Independent Directors, oversees its sustainability agenda, including monitoring its climate change mitigation efforts and targets. The senior management leadership takes responsibility for driving the implementation of this sustainability strategy. The management and Board also oversee the progress regularly.
Environmental Policy and Management System
The comprehensive Environment Management System of Ambuja Cements aligns policies, procedures, and practices with the industry's best standards, allowing it to proactively address climate risks, minimise waste generation, and champion recycling. The Company actively advocates for integrating climate change measures into national policies, reflecting its commitment to broader environmental initiatives and sustainable practices.

Environmental Policies
Ambuja Cements has a set of policies concerning the environmental dimension of ESG.

- Climate Change Policy
- Energy Management Policy
- ESG Policy
- Environment Policy
- Water Stewardship Policy
- Resource Conservation Policy
- Bio-Diversity Policy
The policies are applicable to all operations of the Company and the implementation is overseen by the Corporate Responsibility Committee (CRC). The CRC consists of Independent Directors and is accountable to the Board.
All Ambuja Cements plants have the following management systems in place. The audits take place regularly and the certifications are periodically renewed.
by 2050 with near-term (2030) validated targets
Renewable and green energy used
Scope 1: 559 kg/tonne of cementitious material
Of waste derived resources used
Water-positive
Plastic negative
Trees planted till FY 24
Clinker Factor

Specific thermal energy consumption

Climate and Energy
Climate Strategy
The Company is committed to climate change risk mitigation throughout its business operations and tailoring strategies to adhere to global best practices, aligning with the nation's economic growth aspirations and global climate obligations including, Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) under the Paris Agreement and commitment to United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs). The Company’s climate strategy focuses on key pillars of reducing its carbon footprint, building resilience, strengthening its operations to the impacts of climate change, and developing strong frameworks to integrate climate change considerations.
The Company’s commitment to Net Zero and conserving resources is reflected in its initiatives to reduce carbon footprint, increase share of renewable energy, conserve water, reduce waste and adopt energy efficiency measures.
Climate Governance
Ambuja Cements has a detailed Climate Change Policy in place that mandates the business to be committed to managing climate change risks across its business operations and to develop strategies in line with global best practices. The implementation of the policy is overseen by the Corporate Responsibility Committee (CRC). The committee drives action related to climate risks and reducing carbon footprint and reviews progress in its quarterly meetings. At the corporate level, the ESG team develops the Company’s ESG agenda and supports business functions in driving implementation. In addition to CRC, the Risk Management Committee of the Board oversees the sustainability and ESG risks associated with the business. In recent times, climate-related risks have become important to the enterprise risk management process and the Company has instituted a systematic risk management approach and also reviews progress in their quarterly meetings.

TCFD Disclosure
Ambuja Cements aligns with the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures’ (TCFD) framework and the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) S2 climaterelated disclosures. The Company is committed to identifying and mitigating climate-related risks to safeguard its stakeholders and business operations. This approach includes disclosing climaterelated governance, strategy, risk management and associated metrics and targets.
Climate Risk Management
Ambuja Cements in FY 2023-24 conducted a detailed climate risk assessment study for all its sites and conducted a Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSP) scenario analysis for the identified risks. The anticipated financial risks associated are studied at site-level and organisation-level. Based on these, climate strategy and action are designed to minimise the negative impacts of climate change and build resilience of the business.
Climate Risks - Physical Risks
There are acute and chronic physical risks – acute risks arising from climate-related hazards like temperature extremities, pluvial flooding, coastal flooding, fluvial flooding, drought, cyclone, water stress, etc. and chronic risks from changing weather patterns and rising mean temperature and sea level, etc. These can cause damage to assets, supply chain disruption and other impacts. Detailed analysis of physical risks is carried out for all sites – integrated units, grinding units and bulk cement terminals.
Climate Risks – Transition Risks
Aligned with the TCFD framework, Ambuja Cements considers the following risks:
- Policy and legal
- Technology
- Market
- Reputation
Climate Related Scenario Analysis
For the identified climate risks, Ambuja Cements conducted a Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSP) scenario analysis. The Company undertook scenario analysis on SSP1-1.9, SSP1-2.6, SSP2-4.5, SSP3-7.0 and SSP5- 8.5. By the scenario analysis, the Company tried to understand and capture a wide range of possibilities and encompass different levels of risk, uncertainty and volatility. The Company’s aim is to make certain that its assets and operations are equipped and capable of managing climaterelated risks effectively and take advantage of opportunities that arise as a result.
Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation measures are designed in accordance with the climate risks faced by the business. The Company implements routine inspection and monitoring protocols to emergency response plans, health and safety protocols, effective communication protocols, evacuation plans, etc. The Company also considers annual weather forecasts in its global supply chain decisions to mitigate the risk of delays in sourcing fuels and machinery due to natural calamities. To mitigate the risks of heat waves, the Company has implemented various measures, including scheduling minimal work in warehouses or outdoor areas during peak summer days. The Company conducts mock drills at sites and capacity building for workforce and contractors.
The Company has adequate insurance coverage to protect itself against damages to its business assets or loss of materials in warehouses or transit due to extreme weather events.
Internal Carbon Pricing
Internal Carbon Pricing (ICP) helps the organisation to reduce Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, navigate and mitigate the potential financial impacts of existing and anticipated GHG regulations, drive low-carbon investments and energy efficiency within the organisation. The financial impacts of various risks are quantified at each site and then aggregated at organisation level. The projects are evaluated for their GHG emissions and technology selected for new projects are selected in a way that these are energy efficient and low on carbon emissions. The Company leverages ICP as a strategic tool to align with stakeholder expectations and catalyse behavioural changes within the Company’s operations.

Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHG)
The Company monitors and reports carbon emissions from all manufacturing locations, including integrated cement plants, mines, grinding units, and bulk cement terminals, aligned with GHG Protocol greenhouse gas accounting standards. The direct GHG emissions of cement plants almost entirely consist of CO2. The contribution of other non-CO2 greenhouse gas emissions almost negligible.
Total Scope 1 emissions in FY 2023-24
Total Scope 2 emissions in FY 2023-24
Net Zero Commitment
Ambuja Cements is a leader in climate action and sustainable practices in the sector. The Company intends to significantly contribute to the country’s achievement of net zero emissions. The Company is committed to net zero by 2050. The Near Term (2030) targets are already validated by SBTi in line with a well-below 2°C trajectory. The 2050 targets for Net Zero are under validation by SBTi. As Scope 3 accounts for less than 40%, only Scope 1+2 emissions decarbonisation pathways are to be validated by SBTi. The Company is also committed to the GCCA Roadmap for Net Zero Concrete by 2050. These commitments warrant that the Company is making steadfast progress toward a net zero and sustainable future.
SBTi Validated Targets
The Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) mobilises companies to set science-based targets and boost their competitive advantage in the transition to the low-carbon economy. It is a partnership between CDP, the United Nations Global Compact, the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Wildlife Fund (WWF).
Ambuja Cements is committed to SBTi to reach net zero by 2050. The Company’s 2030 targets are duly validated and approved by the SBTi on September 23, 2021, and can be referred at https:// sciencebasedtargets.org/targetdashboard. The targets include emissions from captive power plants (CPP). This approach demonstrates the Company’s dedication to reducing its carbon footprint and embracing sustainable practices.
Promising Capacity Expansion Benefit in Godda, Jharkhand
Ambuja Cements plans to Ambuja Cements commits to reduce Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions by 21% per tonne of cementitious materials by 2030 from a 2020 base year. With this target, Ambuja Cements commits to reduce Scope 1 GHG emissions by 20% per tonne of cementitious material and Scope 2 GHG emissions by 43% per tonne of cementitious materials in this timeframe. The target boundary includes biogenic emissions and removals from bioenergy feedstocks. (Refer https://sciencebasedtargets. org/target-dashboard)
Performance on SBTi Targets
Net Zero Roadmap
The net zero roadmap at Ambuja Cements Limited aligns with its SBTi commitment and GCCA 2050 roadmap for the cement and concrete industry.
Potential CO2 Reduction using Cement and Concrete Levers in 2050
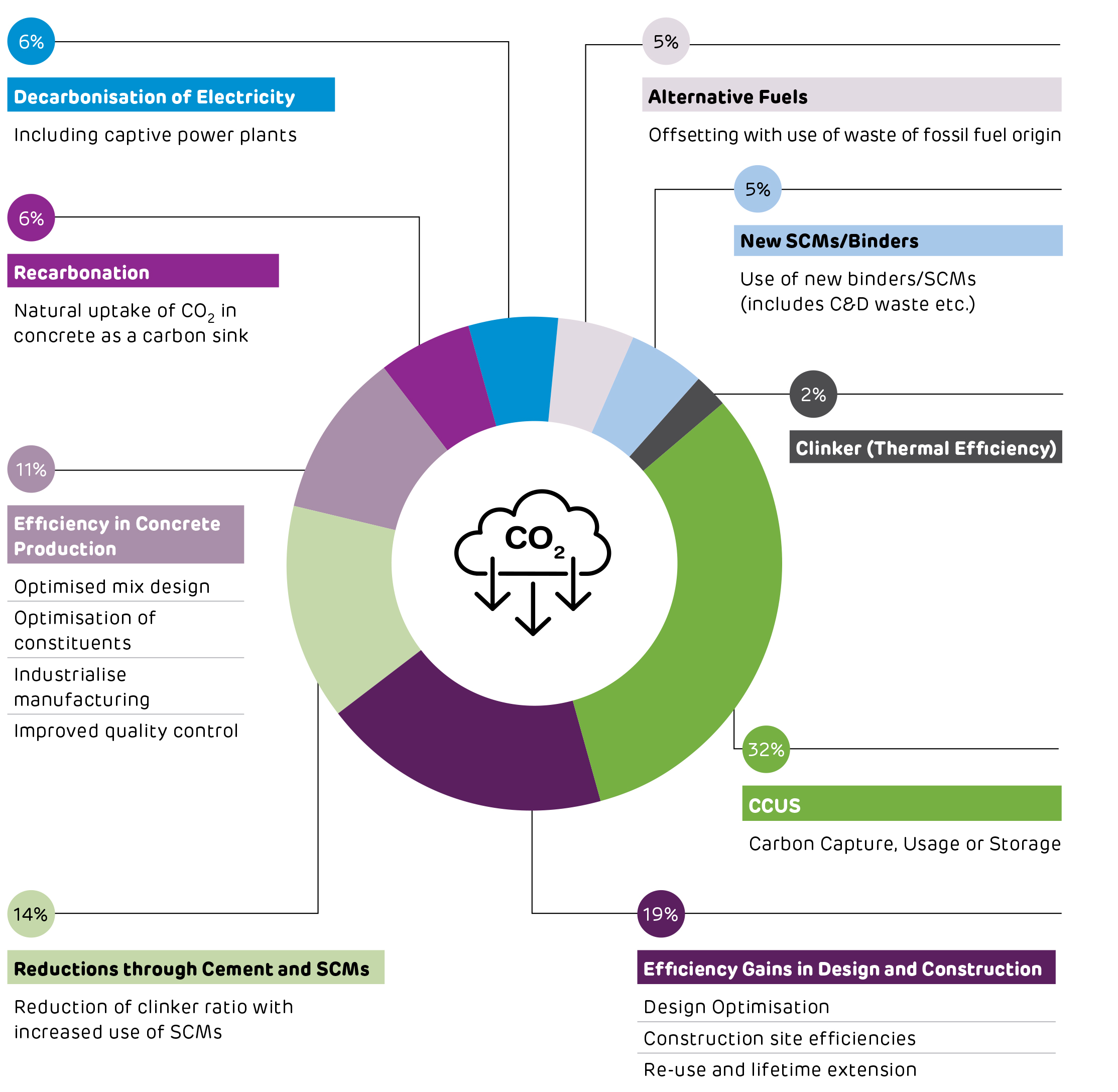

Decarbonisation Levers at Ambuja Cements
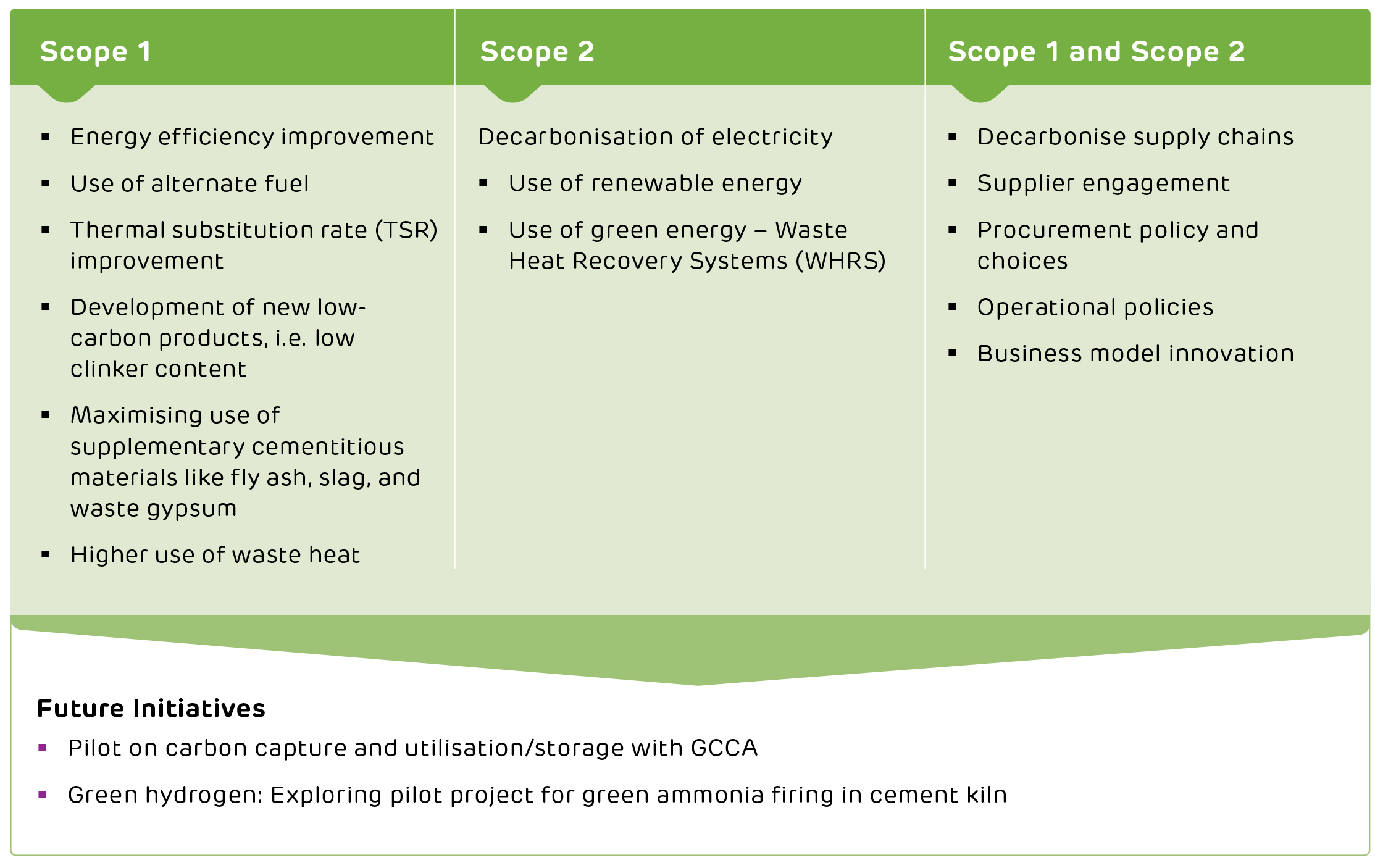

Energy Management
Cement is an energy-intensive sector. Efficient energy management is essential in controlling operational costs and reduce carbon footprint. Ambuja Cements regularly monitors the energy performance at all its sites, which is discussed in the monthly management meetings. Efforts are made to continuously improve the energy performance of the Company.
Energy Consumption
Energy consumption is an important indicator, and Ambuja Cements continuously strives to reduce energy footprint across all its businesses. The businesses rely on a combination of energy sources (fossil fuels, alternate fuels, renewable energy, and waste heat recovery systems) for their operations. The Company continuously tracks energy consumption across facilities and equipment which helps map the consumption pattern to structure and prioritise energy conservation initiatives.
Total energy consumed in FY 2023-24
Total energy consumed from renewable sources in FY 2023-24
Total energy consumed from renewable sources in FY 2023-24
of clinker specific thermal energy consumption
of cementitious material Energy intensity
of cement specific electrical energy consumption
Climate and Energy Management Initiatives
In climate and energy management, the Company has undertaken multiple initiatives such as:
Enhancing the energy efficiency of operations
Using alternative fuels (Co-processing)
Waste heat
recovery systems
Renewable
energy
Green
products
Enhancing Energy Efficiency of Operations
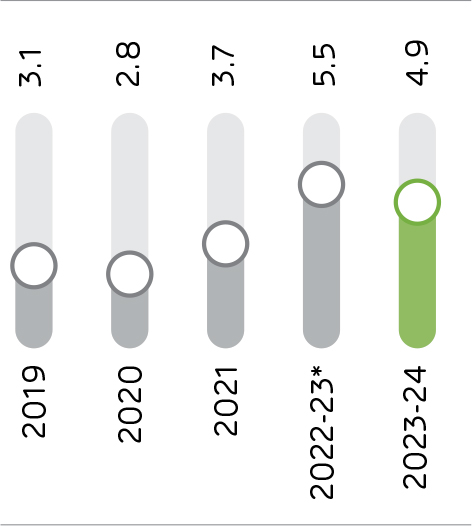
The Company has continuously invested in reducing thermal and electrical energy consumption per tonne of cement produced. Many of its plants fall under the Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) scheme, a regulatory instrument in India to reduce specific energy consumption. The Company’s specific thermal energy consumption has reduced from 760 kCal/kg of clinker produced in 2019 to 752 kCal/kg of clinker produced in FY 2023-24. The target is to reduce it to 710 kCal/kg of clinker produced by 2030.
PAT Scheme to Reduce Specific Energy Consumption
Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) is a regulatory instrument in India to reduce specific energy consumption in energy-intensive industries. It has an associated market-based mechanism to enhance cost-effectiveness by certifying excess energy savings which can be traded.
Under PAT, specific high energyintensive industries are identified as designated consumers within certain key sectors, who must file energy consumption returns every year and regularly conduct mandatory energy audits. The essential tasks in the mechanism are to set the specific energy consumption norms for each designated consumer in the baseline year and in the target years, devise a verification process for specific energy consumption, find ways of issuing the energy savings certificates, operationalisation of the trading process for energy savings certificates in addition to the compliance and reconciliation process for energy savings certificates. The outcomes are in the form of energy savings and subsequent carbon savings.
At Ambuja Cements, the Maratha, Suli, Rouri, Ambujanagar, Ropar, Rabriyawas, Bhatapara, and Sankrail plants are designated consumers. All designated consumers have achieved their PAT target. Suli and Rouri achieved their PAT target by purchasing energy savings certificates.
Thermal Energy Efficiency
(kCal/kg of clinker produced)
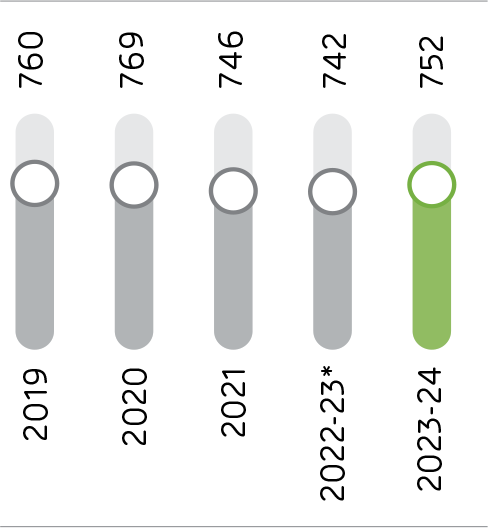
*Note: The Company had changed its financial year end from December 31 to March 31 in FY 2022-23. Therefore, the figure for FY 2022-23 is for 15 months and not comparable with the figures for the 12 months year ended March 31, 2024.

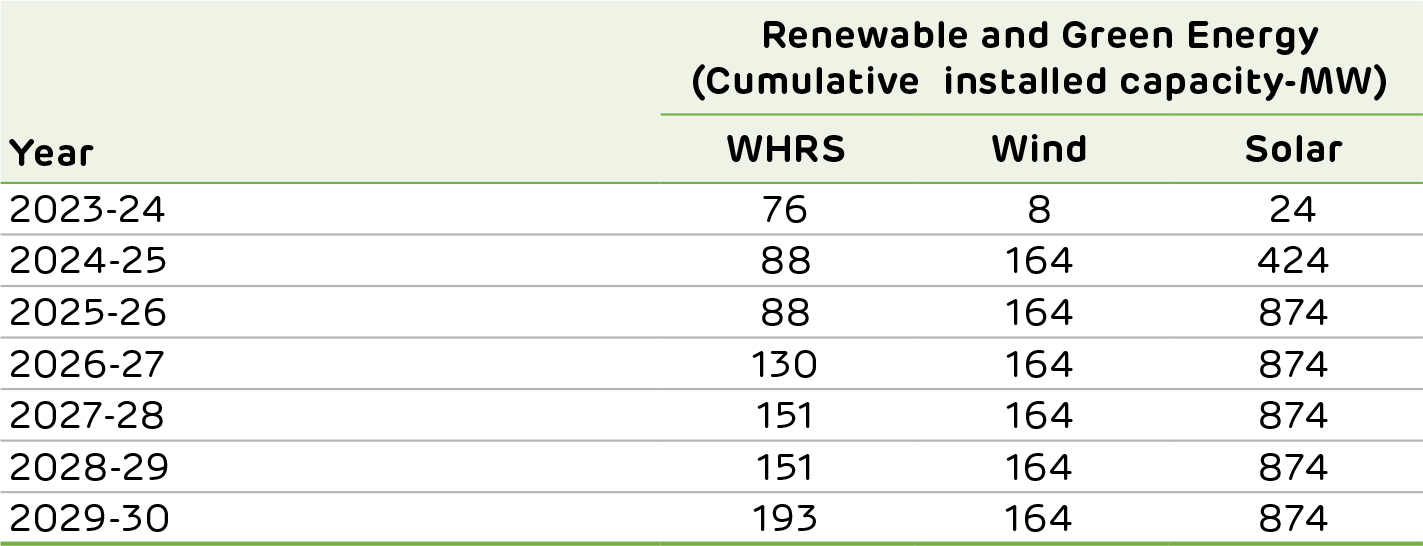
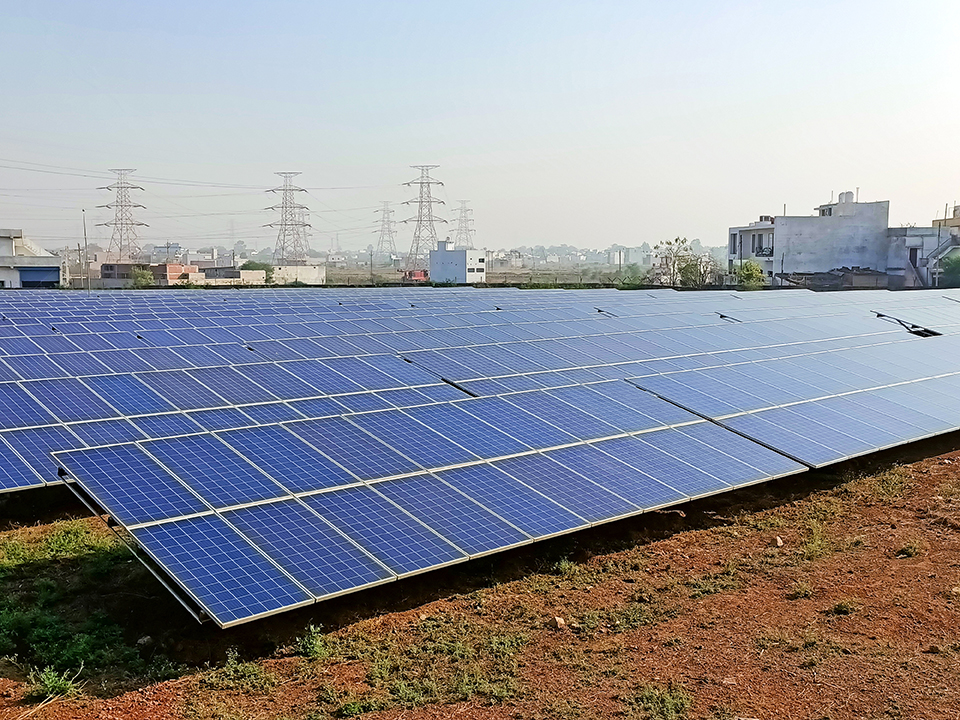
Renewable and Green Energy
Energy consumption significantly contributes to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the cement business. Ambuja Cements is making sizeable investments in renewable and green energy to reduce its carbon footprint. This will lower its dependence on conventional electricity from grids and substantially shrink its carbon footprint. The green power share will increase to 60%, to be the largest in the industry with the planned expansion capacity. Ambuja Cements' renewable energy portfolio majorly includes solar and wind energy and WHRS in green energy. The planned enhancement on installed capacity is below.
This ambitious target reflects the Company’s determination to reduce its carbon footprint, promote clean energy practices and contribute to a more sustainable future. These initiatives are pivotal parts of a broader vision which will help Ambuja Cements achieve the leading share of renewable and green energy among its peers.
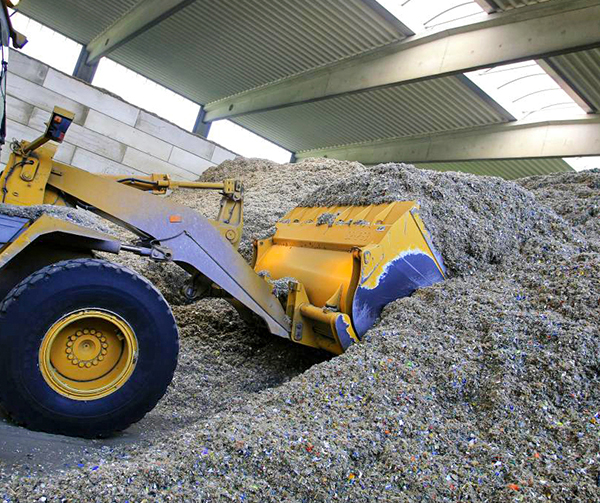
Alternative Fuels (Co-processing)
Ambuja Cements, through its waste management arm Geoclean, takes a sustainable approach to managing industrial, agricultural, and municipal waste. Leveraging coprocessing technology, Geoclean ensures the complete recycling and recovery of resources from waste. Ambuja Cements has invested significantly in upgrading its preprocessing and co-processing infrastructure, transforming highly diverse waste streams into a homogeneous mix suitable for co-processing in cement kilns. This process converts waste into an alternative resource, reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels, conserving natural resources, and cutting greenhouse gas emissions.
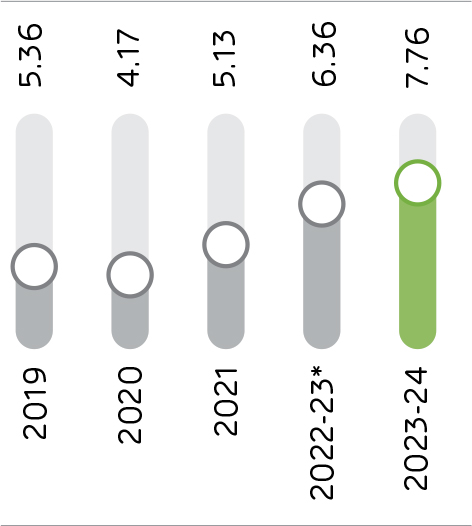
The Company successfully co-processed approximately 0.49 million tonnes of alternative fuels in the reporting period, substituting 7.76% of the total thermal energy.
Alternate fuels used in FY 2023-24
*Note: The Company had changed its financial year end from December 31 to March 31 in FY 2022-23. Therefore, the figure for FY 2022-23 is for 15 months and not comparable with the figures for the 12 months year ended March 31, 2024.

Waste Co-processed
(lakhs tonnes)
Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR)
The thermal substitution rates or co-processing rates are increasing over the years and Ambuja Cements has a target to reach 23% by 2030.
TSR
(%)
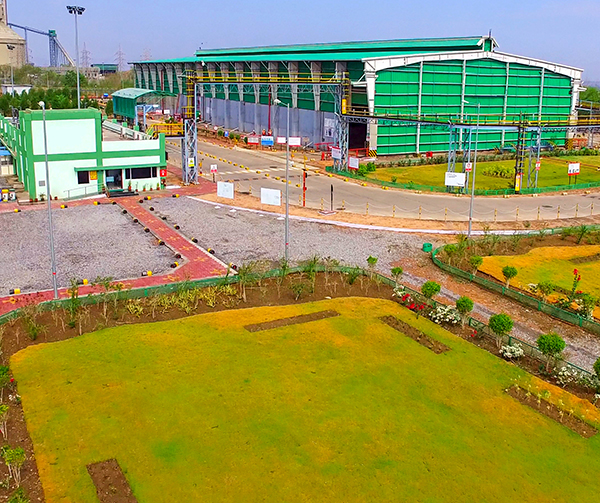

Co-processing of Waste – Geoclean
Through the Company’s waste management arm, Geoclean, Ambuja Cements is at the forefront of addressing the societal challenges posed by growing volumes of waste. As India's leading provider of industrial, agricultural, and municipal waste management services, Geoclean offers sustainable solutions to these sectors. Geoclean supports its customers by managing waste responsibly and cost-effectively, providing services such as guidance, assessment, logistics support, pre-processing, and final treatment through co-processing. It diverts significant volumes of waste from landfills with tailored solutions across various industrial segments and by collaborating with municipalities and local waste management agencies to manage combustible fractions of municipal solid waste (MSW) sustainably. The Company’s pre-processing and co-processing facilities, equipped with modern waste-handling mechanisms, contribute to the move towards a closed-loop circular economy, ensuring a more resource-efficient future.
Mr Dinesh Kumar Poonia
Dy. Manager | EHSS - Environment, Health, Safety & Sustainability
Mankind Pharma Limited
Mankind Pharma Limited, is engaged in manufacturing and distribution of pharmaceutical formulation products. Waka, Namchi Sikkim. With our strong focus on sustainability, we wanted to manage Process Waste & ETP Sludge in environmentally safe manner. Co-processing by Geoclean provided a sustainable and cost-effective technology at the right time with zero residue for landfilling. Professional services and facilities provided by Geoclean are reliable and perfectly suited for our needs and it makes us believe that we will have a long-term association with Geoclean.
Mr Arjun Dahiphale
Distribution Optimisation Specialist
Fererro India Pvt Ltd
At Fererro India Pvt Ltd, with our strong focus on sustainability, we wanted to manage ABC waste in environmentally safe manner. Coprocessing by Geoclean provided a sustainable and cost-effective technology at the right time with zero residue for landfilling. Professional services and facilities provided by Geoclean are reliable and perfectly suited for our needs and it makes us believe that we will have a long-term association with Geoclean.
Mr Parag Kamboj
Purchase Manager
Lenskart
Geoclean’s expertise in sustainable waste management and state-of-the-art technology makes them an invaluable partner for us. We appreciate their commitment to a cleaner planet and the seamless integration of their solutions into our operations. Through coprocessing our waste in cement kilns of Ambuja we are proud to ensure that we are contributing towards a circular economy and diverting our waste from landfills, thus creating a cleaner future.

Green Products
Ambuja Cements is the industry leader in manufacturing and selling blended cement, that is green with a much lower clinker factor. This not only helps the environment by using the slag and fly ash but also helps build durable and strong structures for the nation. More than 85% of the Company's production is in blended cements. The Green products of the Company are duly certified by GRIHA (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment), a national green rating system of India.
Air Emissions
Apart from greenhouse gas emissions, the combustion of fuel in operations also generates air pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur oxide (SOx), which contributes to the environmental impact of the industry. Apart from this, businesses contribute particulate emissions due to the burning of fuel and the movement of vehicles.
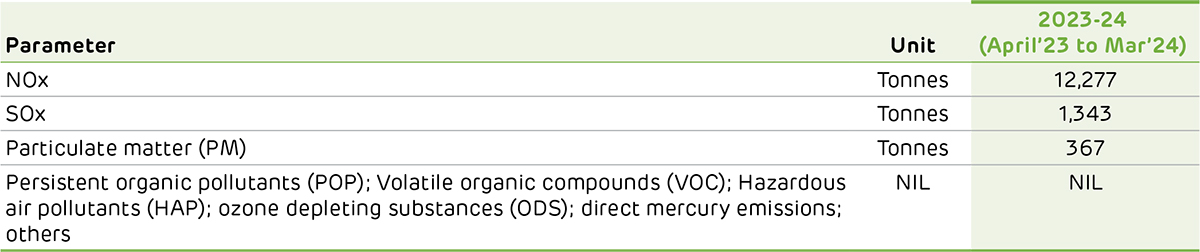
Ambuja Cements has installed air pollution control measures like electrostatic precipitators and bag filters for flue and process emissions. The Company has installed closed conveyor belts for the transfer of material. Moreover, Ambuja Cements undertakes dust suppression measures like water sprinkling to control dust. The Company has also installed continuous emission monitoring systems at all plants to monitor SOx, NOx, dust/particulate matter, and other significant emissions from all its kilns/raw mill stacks. The Company digitally displays the results at all the monitoring locations.
Water Management
Water is one of the scarce natural resources and is one of Ambuja Cements' primary material topics and a key pillar for the sustainable development plan 2030. Cement manufacturing is a dry process. The Company uses water in cooling, dust suppression, and human consumption. The Company recognises the importance of responsible water management in ensuring the long-term viability of its operations and meeting the needs of the communities in which it operates. Ambuja Cements has implemented a robust water stewardship policy to ensure its responsible management. The Company's top priority is the protection and conservation of water resources.
At the heart of the Company’s approach to effective water stewardship is a focus on continuous monitoring and measuring critical water-related factors such as withdrawal, consumption, recycling, and final disposal. Ambuja Cements has also set ambitious targets for being water-positive, and it regularly tracks and reports on its progress towards their goal. Through the water stewardship efforts, the Company aims to contribute to a more sustainable future for all, where there is assured access to clean, safe, and abundant water for future generations. The water stewardship framework has the following objectives:
- Reducing Dependence on Freshwater: Ambuja Cements seeks to minimise its reliance on freshwater resources for its operations
- Community Water Security Extending beyond Business Interests: Ambuja Cements is committed to ensuring water security for communities residing beyond its immediate boundaries
- Being Water-positive: The aim is to continue being water-positive through sustainable water management practices
Fresh water consumption from rainwater harvested
Water-positive
Water Withdrawal and Consumption
While the Company’s operational sites rely on diverse water resources to meet their needs, it is aware of the importance of minimising its impact on shared water sources. To achieve this, the Company continuously evaluates and optimises its water withdrawal processes, aiming to implement efficient and sustainable water management practices. By actively adopting efficient water management practices, Ambuja Cements ensures it uses water judiciously and responsibly.
Fresh water consumed
Water Intensity
Ambuja Cements has undertaken an ambitious target to reduce the intensity of freshwater utilisation per tonne of cement produced. Water intensity has significantly improved over the years, and the Company is likely to achieve its target much ahead of time. These achievements underscore its relentless pursuit of water efficiency and responsible resource utilisation.
As part of the Company’s sustainable development plan for 2030, it has set a target to become 10x water positive by 2030 and it is on track to achieving this target.
Fresh water consumption per tonne of cementitious material in FY 2023-24
Water Recycling and Reuse
As part of the Company's commitment to sustainability, it has implemented robust wastewater recycling and reuse practices across its units. These initiatives aim to maximise water efficiency, minimise its reliance on freshwater sources, and reduce its water footprint. The Company's units have effectively implemented recycling systems and using recycled water for dust suppression and gardening.
Water recycled/reused

Wastewater Discharge
The wastewater generated at plants is treated and recycled for gardening and dust suppression activities. There is no discharge of wastewater outside the premises. Ambuja Cements has effectively minimised and conserved its water footprint by adopting these practices.
Water recycled/reused
Rainwater Harvesting and Conservation:
Recognising that water conservation is a collective responsibility, Ambuja Cements engages with developers and communities to promote water conservation practices that align with its water management strategy. The initiatives include the following:
- Using many of the Company’s closed mine pits for water conservation by rainwater harvesting and groundwater recharge to ensure water availability for livelihoods
- Engaging with rural communities to revive village ponds
- Executing rainwater harvesting in communities to ensure drinking water security
- Partnering with the government for water conservation projects like check dams
- Associating with developers for rainwater harvesting in projects
- Developing an in-house modular (zero-water) curing solution and successfully implementing it in around 2,327 sites over the past year, leading to around 28 million litres of water-saved
- Undertaking water use efficiency measures, ensuring more crop per drop
Water recycled/reused

Waste Management and Circular Economy
The Company adheres to the principles of sustainable consumption of resources while reducing waste generation and complying with the tenets of circular economy. Ambuja Cements prioritises waste management by implementing industry best practices and exceeding regulatory requirements. The Company aims to minimise the negative impacts of improper waste handling by adhering to applicable environmental laws.
Waste Generation
Ambuja Cements aims to minimise waste generation. All waste generated by the businesses is carefully collected and segregated at the source, categorised as either hazardous or non-hazardous. The Company stores these waste types separately in designated waste storage yards. In addition, the Company uses a large quantum of waste-derived resources, reducing its dependence on mined resources and, simultaneously, preventing their disposal into the environment.
Following types of wastes are generated by the Company:
- Plastic waste
- E-waste
- Bio-medical waste
- Construction and Demolition waste
- Battery waste
- Other hazardous waste
- Non-hazardous waste
Total waste generated
of cementitious material
Hazardous waste sent to landfill
![]() For more details of waste generation,
please refer to BRSR, Principle 6,
Question 9.
For more details of waste generation,
please refer to BRSR, Principle 6,
Question 9.
Waste Management Measures
The Company minimises waste disposal through maximising recycling and reusing efforts. The Company also ensures proper disposal of E-waste, biomedical waste, scrap, etc. through authorised recyclers registered with the regulatory agencies. At most plants, plastic waste and used oil is co-processed in cement kiln and there is no disposal of waste to landfills. Some of the waste management initiatives include:
- Plastic waste is mainly disposed through co-processing by the Company and a very small quantity like burst bags through authorised scrap dealers
- Bio-medical waste is disposed through incineration at authorised Common Biomedical Waste Treatment Facilities
- E-waste is recycled through authorised recyclers
- Hazardous waste (used oil, discarded drums) is reused at plant or is co-processed in cement kiln and the quantity which cannot be co-processed is sent to common authorised facility
- Scrap is sold to authorised vendors
- Mining overburden is repurposed and used for backfilling within the mines
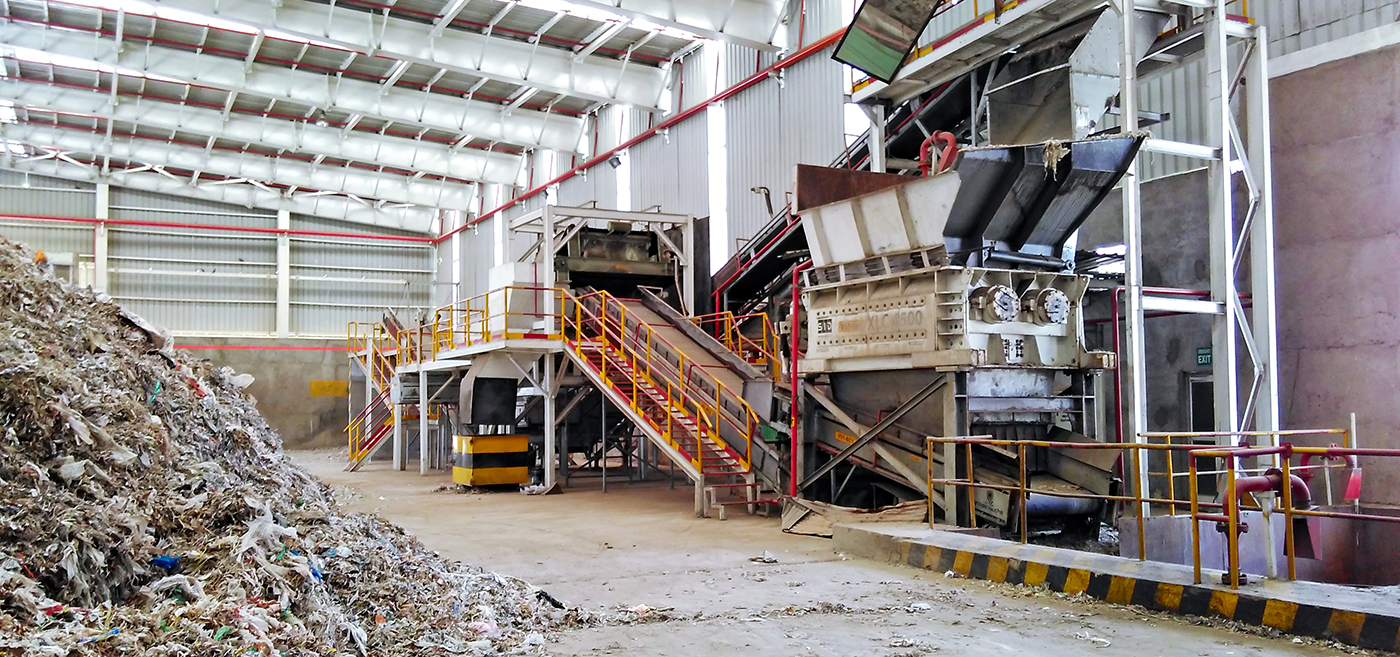

Being Plastic Negative
In a resounding commitment to environmental sustainability, Ambuja Cements proudly embraces a 'Plastic Negative' ethos. The Company leads the charge with an impressive 8x plastic negative impact. It means that it removes 8x more plastic waste from the environment through coprocessing than what is added by its plastic packaging bags. This remarkable achievement signifies its dedication to curbing plastic pollution and actively contributing to a cleaner future.
Plastic negative
Waste-derived Resources
The Company uses a large quantum of wastes from other industries and reduces its dependence on mined resources and, simultaneously, preventing their disposal into the environment. This includes fly ash, slag, gypsum and other waste. In FY 2023-24, the Company used 8.6 million tonnes of waste derived resources. Out of this, 0.49 million tonnes of waste was used for co-processing.
Waste-derived resources in FY 2023-24
Biodiversity Management
Biodiversity management is a key focus area in the Company’s materiality assessment. Ecosystems that are in good health are better equipped to withstand natural disasters. The crucial ecological systems that businesses and society depend on are more effectively safeguarded when biodiversity is robust.
Ambuja Cements understands the importance of addressing the impacts of its operations on biodiversity and has developed a comprehensive biodiversity policy. This policy is a guiding framework for identifying and evaluating biodiversity-related impacts and risks at project sites throughout their lifecycle. By adhering to this policy, the Company aims to minimise its ecological footprint and contribute to biodiversity conservation and sustainable management.
Biodiversity Risk Screening
This assessment aims to identify any sensitive biodiversity risks that the business operations may cause. The Company avoids undertaking operations near the World Heritage Sites, protected areas, sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves. The Company’s operating sites are not adjacent to indigenous peoples’ territories.
The Ambujanagar plant, though not within 10 kilometres of sensitive biodiversity areas, has one of its captive mines, which falls within 10 kilometres of the Gir National Park. The Company has the environmental clearance for it, and all the operations comply with statutory conditions. At Darlaghat plant, protected areas like the Majathal Sanctuary and Darlaghat Conservation Reserve are within 10 kilometres of its mining or plant operations. Non-sensitive sites like Rabriyawas, Maratha, and Bhatapara have also prepared biodiversity action plans to protect and enhance biodiversity.
Biodiversity Impact Assessment
As part of the Company’s commitment to biodiversity conservation, it integrates biodiversity impact assessment into the environment impact assessment process for both greenfield and brownfield projects requiring clearance from the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MOEFCC) or State Environment Impact Assessment Authority (SEIAA). For all the sites for which environmental clearance is mandatory, the Company conducts comprehensive baseline studies on flora and fauna before project commencement, focusing on endangered and nationally protected species within the project’s influence area, as outlined in the terms of reference.
Ambuja Cements assesses any potential impacts or risks to biodiversity resulting from project activities. These studies are available on the PARIVESH portal of the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MOEFCC), Government of India. Some of the key potential risks evaluated include:
Upstream
- Disturbance to the habitat from land use change and construction activities
- Introduction of invasive species because of the movement of goods and vehicles
Direct Operational
- Risks of pollution
Downstream
- Movement of vessels, traffic, cargo handling that may generate significant noise and vibration disrupting the behaviour, feeding patterns, and communication of species
Biodiversity Management Plan
Ambuja Cements has prepared a biodiversity management plan to protect and enhance biodiversity around the Company’s operations. The Company has based this plan on the baseline study on biodiversity conducted for the project influence area and the likely impacts of the project on biodiversity. This plan encompasses measures to protect natural habitats, restore ecosystems, and enhance biodiversity. The plan includes habitat protection, species protection, ecosystem restoration, stakeholder engagement, and monitoring. Ambuja Cements is committed to enhancing biodiversity, minimising negative impacts, and contributing to the conservation and sustainability of biodiversity in its operating regions through this plan.
The Company partners with local experts and forest department to develop comprehensive biodiversity action plans. For Darlaghat, the Company has prepared a wildlife conservation plan for key species which the State Government has approved the plan.
Key Aspects of the Company’s Biodiversity Management Plan
- Improving degraded habitats across sites through targeted habitat management plans
- Working closely with the community and government bodies to adequately manage the planted and rehabilitated areas
- Partnering for the management of any other adjoining offset areas
- Turning regenerated areas into natural habitats by adopting new forestry practices
- Carrying out mining operations and raw material transportation only during the daytime near protected areas
- Providing mine tippers with a multi-cap covering system
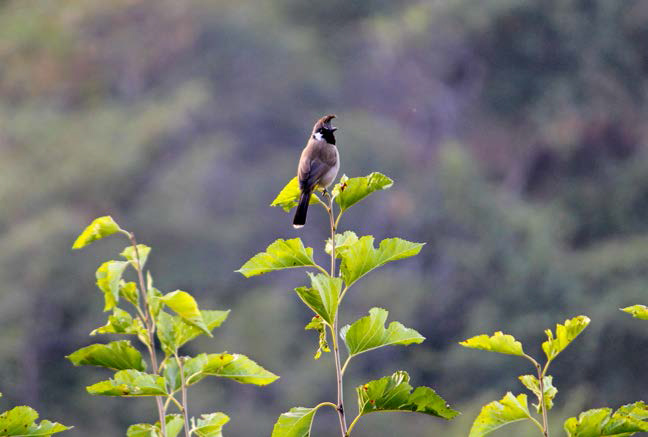

Rich Biodiversity in and around Ambujanagar Plant
The green belt developed around the plant and tree plantations carried out at township and surrounding areas have led to a rich biodiversity in and around Ambujanagar. In addition to this, we plant trees on the mine lease boundaries and on closed mines which leads to preservation and improvement of regional biodiversity. Some of the closed mine pits are used for water conservation and ground water recharge. These waterbodies attract a number of migratory birds. As a result, a wide variety of flora and fauna is seen in and around the plant.
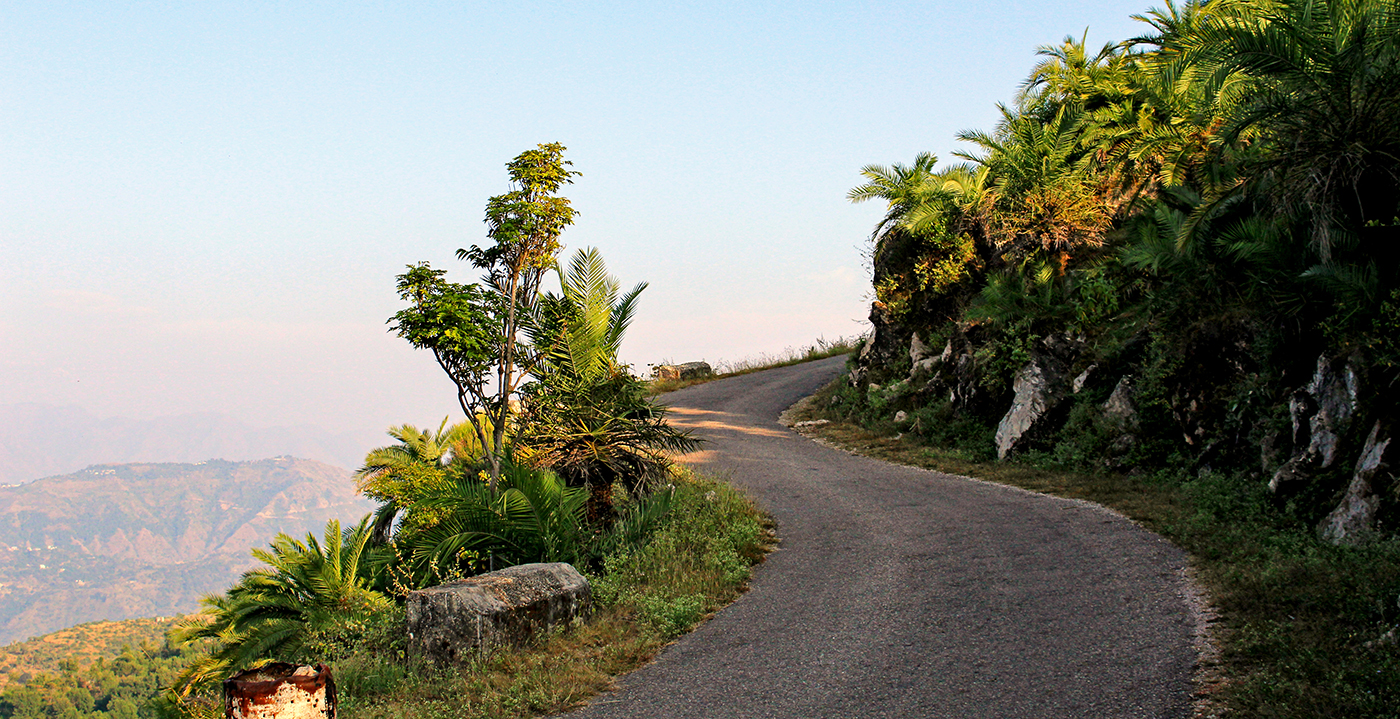

Initiatives for Biodiversity Conservation
Ambuja Cements proactively implements measures at its plants and mining sites to ensure the local biodiversity is not disturbed.
Tree Plantation Targets: The Adani Group has pledged on the World Economic Forum’s Trillion Trees Platform (1t.org) to grow 100 million trees by 2030. As a part of this target, Ambuja Cements will grow 2.42 million trees by 2030.
No Net Loss to Biodiversity: The Company is committed to achieving ‘positive change in biodiversity’ (net positive impact) by 2030. Ambuja Cements is aligning it’s no net loss to biodiversity approach with the Taskforce on Naturerelated Financial Disclosures framework to guide its efforts in preserving biodiversity. Achieving no net loss to biodiversity involves a comprehensive and sciencebased approach.
Signatory of IBBI: Ambuja Cements is a signatory to the India Business and Biodiversity Initiative (IBBI) of the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH. This commitment demonstrates its active participation in collaborative efforts with other businesses and stakeholders to promote biodiversity conservation and sustainable practices.
https://sustainabledevelopment.in/ ibbi-membersGreen Belt around Mining Sites: Green belts in and around the plant and mine areas have transformed the land around the Company’s sites into greener habitats. The green belt counteracts the negative impact of mining by reducing dust pollution and absorbing carbon emissions.
Water Harvesting in Mine Pits: Water conservation in mine pits in the rainy season helps recharge the groundwater table; the increased availability of water enables people in the water-scarce regions of Gujarat and Rajasthan to grow multiple crops during a longer period of the year, improving their prospects of earning livelihoods. It also preserves the biodiversity of the region. Moreover, numerous migratory birds visit these sites.
Quarry Rehabilitation and Biodiversity Management
As part of the Company’s quarry rehabilitation and biodiversity management, it initiated a new baseline biodiversity assessment of the sites through a Biodiversity Indicator and Reporting System (BIRS) developed by experts from the International Union for Conservation of Nature. BIRS is a simple system for assessing the overall biodiversity suitability of a defined site having different habitat types, expressed as ‘site condition class’. It considers the area of every habitat type on a site, the ecological condition of these habitats (including enhancements and threats), and each habitat's uniqueness and environmental importance in the regional context. Ambuja Cements conducted a BIRS assessment for the five sites with mines in 2016-17 and repeated it in 2019-20. The baseline site biodiversity index was measured on a scale of 1 to 4.

Responsible Mining
Ambuja Cements adheres to responsible mining practices to safeguard the environment and biodiversity around its mines. The mines are generally leased mines from government involving no R&R. The Company sources limestone from captive mines near its integrated plants, employing sustainable extraction methods and innovative operational practices.
In Ambujanagar (Gujarat), the Company uses a blast-free, ecofriendly surface miner technique to minimise noise and dust. Other mines employ controlled blasting with high-precision electronic detonators to enhance safety and reduce environmental impact. Scientific mining technologies ensure mineral conservation, and the Company undertakes drilling with dust-suppression measures. Haul roads are maintained to minimise dust emission. At many places, covered conveyor belts are deployed to haul mined material to plant. Ambuja Cements ensures that all mining sites strictly follow health and safety measures. Green belts around the mines and plant areas reduce dust pollution and preserve biodiversity.
The Company trains its team members to work with communities, minimising the impact on biodiversity.

Regulatory Compliance
The Company recognises the importance of regulatory compliance and its role in ensuring responsible and sustainable business operations. Ambuja Cements adheres to a comprehensive range of environmental regulations as a business operating in various sectors. The Company ensures that all necessary permissions and approvals are in place to meet these obligations. To monitor compliance effectively, it utilises the Legatrix software. Some of the key environmental regulations applicable to its operations include:
- Environmental Clearances and EIA Notification, 2006
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
- Noise Pollution (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000
- The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- Hazardous and other Wastes (Management & Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2016
- Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016
- Bio Medical Waste Rules, 2016
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016
- E-Waste Rules, 2016
- The Construction and Demolition Waste Management Rules, 2016
Ambuja Cements' commitment extends beyond mere compliance, as it strives to excel and set a benchmark among its industry peers regarding regulatory adherence and best practices.
![]() Case Study
Case Study

Enhancing Environmentconsciousness with ‘udAAAn’
- The mining team at Darlaghat drastically reduced the cost of diesel through Project ‘Thermol-D’
- Several initiatives have been taken to increase the biodiesel consumption in the mines
- Conducted several initiatives to reduce power consumption, optimise product residue and minimise wastes
- Ambuja Cements has enhanced the ILC Coal firing system, leading to increased AF feeding and independent operation of Coriolis. This improvement involved increasing the Coal Firing blower flow and implementing modifications to the ILC Coriolis system
- The Company increased WHRS capacity to use waste heat as well as improve efficiency












