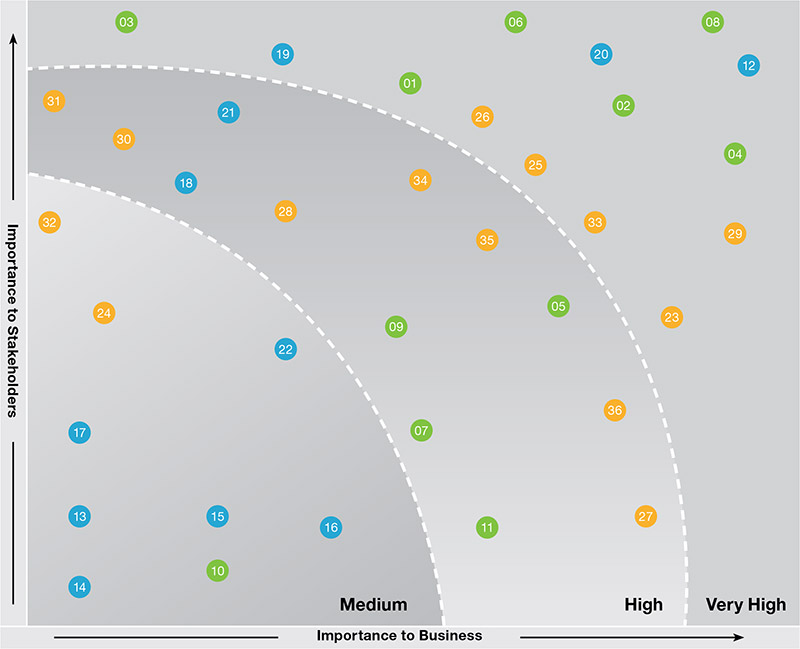
Through a comprehensive materiality assessment, we identify, assess and understand the financial and nonfinancial issues that impact our business and the process by which we create long-term value for our stakeholders. These issues are integral to our planning process and help support the delivery of our business strategy.
We engage in a comprehensive stakeholder engagement exercise, based on a well-defined, closed-loop approach. This includes identification of stakeholders, prioritisation, engagement, strategy development, preparation and implementation of the action plan to complete the feedback loop. The prioritisation of material topics related to performance, people, and planet are well aligned with our strategic pillars.

IDENTIFY
Relevant topics to include in the assessment
PRIORITISE
Topics gathered from the opinions and concerns of our stakeholders
How we assess our materiality issues

DEFINE
Stakeholder groups

REVIEW
Results reviewed internally to ensure their alignment with our business risks and strategy
Why materiality matters?
STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT
The process of stakeholder engagement serves as a tool for understanding the reasonable expectations and interests of stakeholders, as well as their information needs. Systematic stakeholder engagement is likely to result in ongoing learning within the organisation, as well as increased accountability to a range of stakeholders. Accountability strengthens trust between the organisation and its stakeholders.
The materiality assessment process gives insights in understanding current and future risks and opportunities to build a sustainable business strategy.

RISK MANAGEMENT
Materiality assessment is a strategic business tool because it is a fundamental step in understanding material issues which leads to assessment of risks around these topics. Today, enterprise risk management includes risks associated around ESG as well. The World Economic Forum also highlights the increasing interconnectedness among ESG risks with risks in other categories— particularly the complex relationship between environmental risks and social issues.

IDENTIFYING KEY OPPORTUNITIES
Materiality assessment leads to opportunity identification around material issues such as cost savings, efficiency gains, new revenue streams from green products and so on. Materiality helps in creating a lens in understanding opportunities and staying ahead of competitors.