Environment. Being future-ready.
Energy Management GRI-302
Depleting coal reserves and volatility in the Indian rupee has been escalating concerns about coal. To mitigate risks associated with the dynamic fuel market, the Company has developed the ability to switch to the most economical fuel mix. Improvement of energy efficiency at all stages of consumption of coal and other fuels is an ongoing crusade. This has led to increased focus on the use of low-cost waste material like petcoke as fuel. Our ‘Geo 20’ initiative to use costefficient and sustainable green fuel has been going on successfully, reducing our energy costs and carbon footprint. As a long term solution to energy security, we have invested in the construction of new state-ofthe-art storage and pre-processing platforms at or integrated plants to increase the use of alternative fuels and raw materials (AFR).
 Great value is placed on use of AFR, waste heat
recovery (WHR) and use of renewable energy like
biomass. The international standard ISO 50001:2011
is implemented in three integrated and six grinding
plants to further strengthen our energy management
system. At Maratha Cement Works, the MP turbine has
been replaced by an HP turbine, resulting in improved
efficiency and lower power generation cost. Voltage
variable frequency drives (VVFDs) have been replaced
to reduce power consumption. A separate fly ash
grinding and blending unit has been commissioned
at Ambujanagar to produce consistent, high quality
cement and reduce power consumption.
Great value is placed on use of AFR, waste heat
recovery (WHR) and use of renewable energy like
biomass. The international standard ISO 50001:2011
is implemented in three integrated and six grinding
plants to further strengthen our energy management
system. At Maratha Cement Works, the MP turbine has
been replaced by an HP turbine, resulting in improved
efficiency and lower power generation cost. Voltage
variable frequency drives (VVFDs) have been replaced
to reduce power consumption. A separate fly ash
grinding and blending unit has been commissioned
at Ambujanagar to produce consistent, high quality
cement and reduce power consumption.
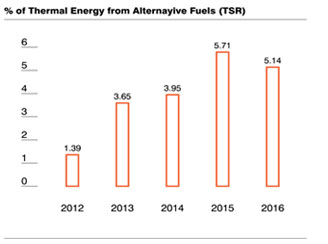
During 2015-16, our thermal energy efficiency remained between 3,107–3,152 MJ/tonne clinker. Electrical energy consumption remained around 77 KWh/tonne cement. Power and fuel costs account for about 21% of our total expense. The cost increase was offset by substituting high cost coal with petcoke in our kilns. Consumption of AFR in the kilns increased to 1.8 lakh tonnes, achieving a thermal substitution rate (TSR) of 5.14% of the total thermal energy which would otherwise have been obtained from fossil fuels. As a result, our coal requirement reduced by about 77,000 tonnes. In addition, 75,000 tonnes of alternative fuels (AF) were used in our captive power plants, taking the total consumption of AF to 2.55 lakh tonnes across all our plants. During the year, 51,405 tonnes of plastic waste were co-processed in our kilns. This was 1.54 times the plastic used in our cement packing bags, making us plastic positive. Ambujanagar led the way by becoming 6.6 times plastic positive; Maratha Cement Works achieved a value of 2.3. The total energy generated from renewable sources stood at 6.5% in 2016, compared to 4.6% in 2015.
Renewable Energy (RE) Performance
Of the total energy generated, 6.5% was from renewable energy sources, compared to 4.6% in 2015. Our renewable energy portfolio consists of a 15 MW biomass-based power plant at Ropar (established in 2005); a 7.5 MW wind power station in Kutch (established in 2011); a 330 KV solar power station at Bhatapara (established in 2012); a 55.14 kWp rooftop solar PV project at the Gurgaon office (established in 2014); and a 6.5 MW waste heat recovery based power generation system at our Rajasthan plant (commissioned in 2015). Ambuja Cement’s captive power plants also use biomass. The Ropar unit produced about 47% of its energy from biomass this year. The renewable energy certificates that we earned, and the power-mix cost optimisation at our plants added value to our power sourcing strategy and RPO compliance. The Company purchased RE certificates equivalent to 21.66 million units (MUs) of non-solar power and 4.65 MUs of solar power in 2016. RE and WHRS projects enabled us to reduce about 65,441 and 26,924 tonnes of CO2 respectively in 2016.
Constant efforts are made to reduce the power, LDO, coal and other fuels consumed per unit of cement produced. Although currently there are no industry standards for energy requirements for the use of cement at the user level, Ambuja Cement will always strive to adopt best practices. GRI 302 (4, 5)