The Risk Management Committee of the Ambuja Board
lays down the procedures for risk assessment and
minimisation and the Board is responsible for framing,
implementing and monitoring the risk management plan of
the Company. The Committee reviewed the risk trend,
exposure and potential impact analysis carried out by the
Management. MD & CEO and CFO have confirmed that
mitigation plans have been finalised and up to date, the
owners have been identified and the progress of mitigation
actions monitored. The Committee met once during the year.
The directors or the highest governance body of the
Company also engage with the risk management process
through bodies like the Risk Management Committee, CSR
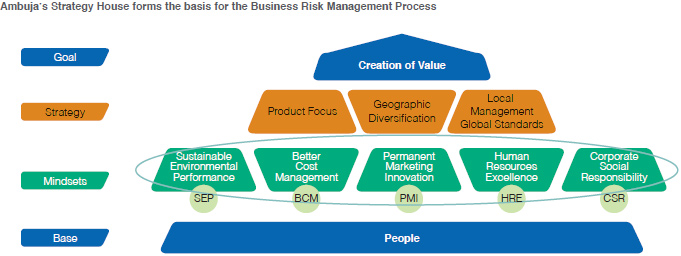
Committee & Compliance Committee. Ambuja has a well
embedded business risk management (BRM) process for
identifying risks and opportunities at corporate as well as
operational levels. The overall objective is to improve
awareness of the Company’s risk exposure and manage it
appropriately. Materiality reviews are conducted in
conjunction with the annual business planning cycle. BRM
includes assessment of social, economic, and
environmental risks. Risk assessment and Management
policy support sustainable business modules for increased
profitability. Our risk management approach incorporates
sustainability; it provides Management with useful data to
identify emerging issues and develope new and better
products and processes. These help protect the Company’s
reputation and improve shareholder value. Sustainability
gives us an opportunity to look at risks in a broader rather
than a traditional risk management framework; this entails
looking beyond economic, strategic, and operational factors
and including social and environmental considerations;
sustainability allows corporations to consider emerging risk
areas and to look for opportunities presented by risks that | are overlooked by other analytical and systems-driven
approaches. A more holistic point of view assures sound
financial management, ethical corporate governance and
transparency with respect to information provided to
employees and other stakeholders. Examples of emerging
sustainability concerns for our industry include climate
change, social justice, depletion of non-renewable resources,
brand damage (including boycotts), shareholder actions
related to sustainability issues and disclosure of historic
environmental liabilities. Sustainability risk management
also requires the evaluation of many aspects of the entity’s
operations that are not part of the most current corporate
programmes. Examples include energy consumption,
emissions of greenhouse gases, water use, waste
generation/ consumption, AFR etc. At Ambuja, we address
many aspects of sustainability, as it improves business
efficiency and boosts profits. Efficient productivity includes
reduced material requirements, reduced energy for
production, lowering of toxic gas emission, improving
recyclability, improving the durability & reliability of
products, and maximising the use of renewable resources.
Implementation of a sustainability programme starts with an
understanding of corporate and regional principles and
values. The fundamental values that unify an entity’s actions
are its way of thinking and its people; these are derived from
where the Company has been, where it is today and its
quest to continue delivering value into the future. The first
step towards implementation is risks/opportunities
assessment, where all the possible risks/opportunities are
identified and then mapped. The next step is prioritising the
risks/opportunities and formulation of action plans which then
take form of projects. One such example is the ongoing
‘Geocycle’ Project.
|